Digital payments have become a normal part of everyday life, and businesses across industries are investing in secure and convenient payment apps to meet growing customer expectations. Whether it is sending money to a friend, paying bills, scanning a QR code at a store, or managing a mobile wallet, users now prefer fast and frictionless digital transactions.
This shift is growing at an impressive pace. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global mobile payment market is valued at approximately 4.97 trillion dollars in 2025 and is projected to reach 26.53 trillion dollars by 2032.
This rapid rise in digital transactions has created a powerful opportunity for fintech startups, banks, and enterprises that want to build their own payment solutions. Payment app development involves more than creating a simple money transfer feature.
It requires strong security, compliance with financial regulations, seamless integration with banking APIs, and a smooth user experience. For many businesses, understanding where to begin can feel overwhelming. In our 15+ years as a financial software development company, we have seen this challenge first-hand.
This guide explains everything you need to know before building a payment app. Learn about the types of payment apps, must-have features, advanced capabilities, the full development process, required compliance standards, cost breakdown, and the technology stack you need to deliver a safe and reliable payment experience.
Contents
What Is a Payment App?
A payment app is a mobile application that allows users to send, receive, and manage money through their smartphones. These apps simplify everyday transactions by replacing the need for cash or cards with fast and secure digital payments.
Whether it is paying a friend, purchasing a product online, transferring money to a bank account, or scanning a QR code at a store, payment apps make financial transactions effortless and accessible.
Payment apps work by connecting a user’s bank account, debit card, or mobile wallet to a secure digital platform. Once connected, users can complete transactions in real time with just a few taps. Most payment apps also include features like transaction history, bill payments, in-app notifications, and biometric authentication to ensure a safe and smooth experience.
Modern payment apps operate through a combination of mobile technology, encrypted communication, API integrations, and banking networks. When a user performs a transaction, the app securely sends the data to the payment processor or bank, verifies the details, and completes the transaction within seconds.
In simple terms, a payment app is a digital tool that gives users control over their daily financial activities while helping businesses deliver a seamless payment experience.
Why Businesses Are Investing in Payment App Development
Building a payment app right now is fundamentally different from five years ago. The barriers have dropped. The opportunity has expanded. The timing is optimal. Here’s why:
Technology has matured
- Payment APIs are now standardized and accessible. You don’t need to build infrastructure from scratch.
- Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure handle scalability automatically. You pay for what you use.
- Security frameworks and compliance tools are available off-the-shelf. Security isn’t something you have to invent anymore.
- Developers experienced in fintech are available for hire. The talent pool exists.
Consumer trust is already built
- People have already trusted payment apps with their money. They’ve moved billions through apps like Venmo, PayPal, and Cash App.
- Your challenge isn’t convincing users that digital payments are safe. That battle is won.
- Your challenge is differentiation. How is your payment app better, faster, or more useful than competitors?
Regulatory clarity is increasing
- Major economies like the US, EU, and UK have established clearer rules for payment apps, digital wallets, and fintech companies.
- Compliance is still important, but you’re not navigating an unregulated wild west anymore.
- Regulatory frameworks create stability and protect legitimate businesses.
- Knowing the rules up front makes planning and budgeting more predictable.
Venture capital is actively funding Fintech
- Investors recognize the market opportunity. They’re backing founders with solid ideas and proven execution.
- Fintech funding reached record levels in recent years. If you have a compelling vision, capital exists.
- If you want to scale fast, the money is available. If you want to grow methodically, that’s possible too.
With the benefits of payment mobile app development clear, let’s explore the different types of payments apps you can develop.
Build a Secure and Scalable Payment App With Our Expert
Take your fintech idea from concept to launch with a team that understands security, compliance, and seamless user experience. We build secure, compliant payment apps trusted by startups and enterprises.

Which Payment App Should You Build? Types of Payment Apps
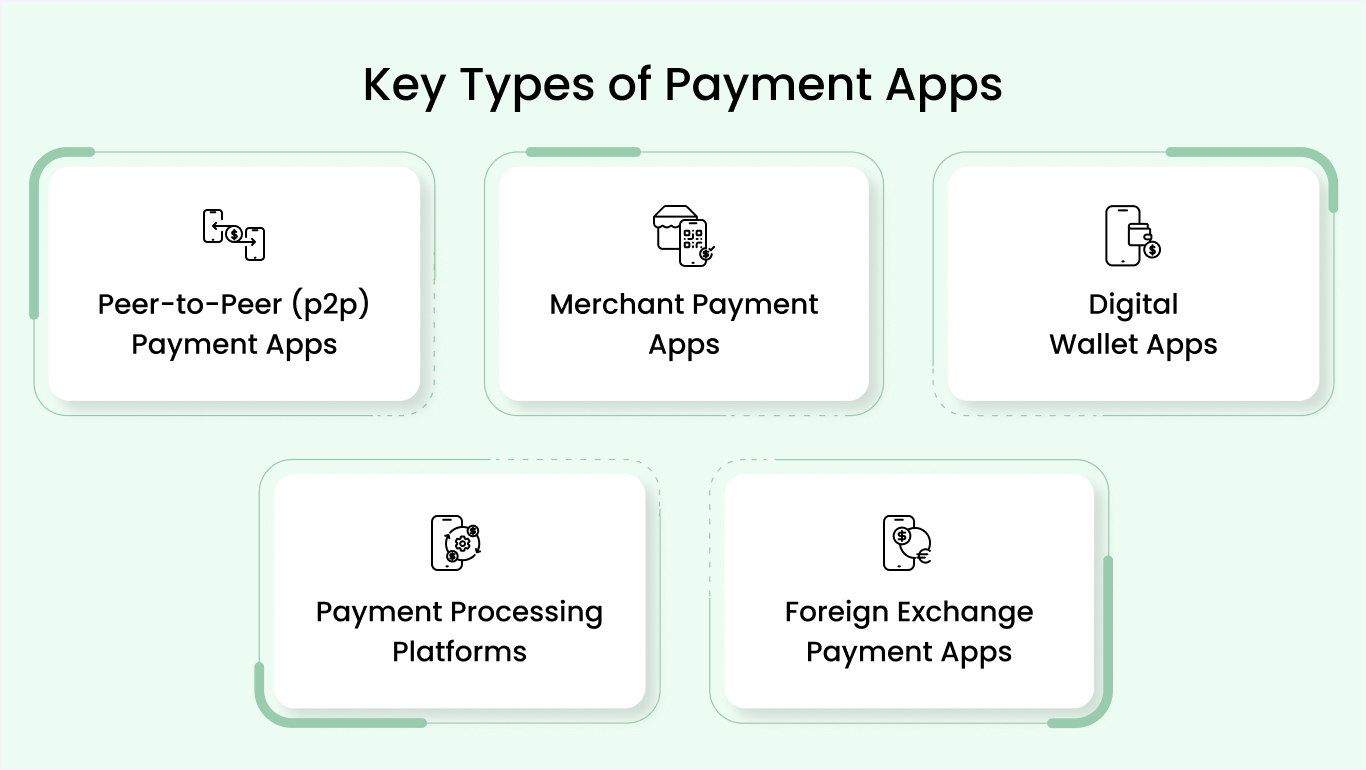
Your payment app development strategy depends on understanding five distinct models. Each serves different markets, requires different resources, and generates revenue differently. Whether building a P2P app, merchant solution, or digital wallet, choosing the right model first determines everything ahead.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) payment apps
P2P payment apps let people send money directly to friends, family, and contacts instantly. Users link their bank accounts or cards, search for recipients by phone or username, and transfer funds with a few taps. Money settles in real-time or within hours. Venmo, PayPal, and Cash App dominate this space globally.
Core capabilities
- User registration and identity verification (KYC)
- Digital wallet for fund storage
- Contact search and friend lists
- Instant peer-to-peer transfers
- Transaction history and receipts
- Social features (payment notes, feed, emojis)
- Multiple funding sources (bank account, card, balance)
- Real-time push notifications
Use scenarios
- Friends splitting dinner bills and restaurant costs
- Roommates paying monthly rent and utilities
- Family members sending allowances and gifts
- Freelancers requesting payments from clients
- Parents paying children for chores and allowance
Merchant payment apps
Merchant payment apps enable businesses to accept customer payments without traditional card terminals. Customers scan QR codes or tap their phones via NFC at checkout. Payments are processed securely in seconds. Funds settle to the merchant’s bank account within hours or days. Square, Stripe Terminal, and PayPal Here are leading examples.
Core capabilities
- Business account setup and verification
- QR code generation for each transaction
- NFC payment acceptance (tap-to-pay)
- Real-time payment processing
- Transaction receipt generation
- Settlement to the merchant bank account
- Sales analytics and reporting
- Refund management
- Multi-location support
- Inventory management integration
Use scenarios
- Coffee shops accepting mobile payments at the counter
- Food trucks processing contactless payments
- Retail stores with point-of-sale systems
- Restaurants enabling table-side payments
- Hair salons and beauty services
Digital wallet apps
Digital wallet apps securely store payment card information, enabling seamless online and in-store purchases. Users authenticate with biometrics or PIN at checkout. Merchants receive payment without seeing sensitive card details. Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay use this model, dominating mobile payment acceptance globally. Digital wallet app development requires robust security protocols and compliance with financial regulations.
Core capabilities
- Secure card storage with tokenization
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint, face recognition)
- PIN-based authentication
- Online payment integration (websites, apps)
- NFC for in-store contactless payments
- Transaction history and receipts
- Card management (add, remove, set default)
- Fraud detection and prevention
- Multi-card support
- Express checkout options
Use scenarios
- Grocery shopping with tap-to-pay at checkout
- Online shopping with one-tap payment
- Ride-sharing purchases (Uber, Lyft)
- Movie ticket purchases online
- Travel bookings and hotel reservations
- Subscription service payments
- In-app game and digital content purchases
Payment processing platforms
Payment processing platforms connect businesses to payment networks at the infrastructure level, supporting billing software development and integration. Developers integrate your API into their apps or websites. You handle tokenization, fraud detection, and routing to card networks. Stripe, Adyen, and Square handle billions in annual transaction volume through this model.
Core capabilities
- RESTful and webhook APIs for integration
- Payment gateway functionality
- Tokenization and card storage
- Fraud detection and prevention (AI-powered)
- Multi-currency support
- Recurring billing and subscriptions
- Real-time transaction reporting
- Webhook notifications
- Settlement management
- Chargeback handling
- PCI DSS compliance tools
- Developer dashboard and testing environment
Use scenarios
- E-commerce platforms accepting online payments
- SaaS applications collecting subscriptions
- Marketplace platforms (Etsy, Shopify) are processing payments
- Booking platforms (Airbnb, hotels) handling reservations
- Online education platforms are collecting tuition
- Streaming services managing subscriptions
Foreign exchange payment apps
Foreign exchange payment apps specialize in cross-border money transfers with minimal markups. Users enter the amount and the destination country. Real exchange rates are quoted upfront. Funds transfer to recipients in local currency via banking partnerships. Wise, OFX, and Remitly dominate this segment, serving diaspora communities globally.
Core capabilities
- Multi-currency support (50+ currencies typically)
- Real-time exchange rate quotes
- Recipient bank account verification
- KYC and AML compliance
- Multiple funding options (bank transfer, card, balance)
- Settlement via local banking networks
- Transaction tracking and status updates
- Recurring transfer setup
- Low fees and transparent pricing
- Mobile and web interfaces
- Account verification (ID, address, phone)
Use scenarios
- Migrant workers sending money to their families overseas
- Freelancers converting earnings to home currency
- International students paying tuition abroad
- Remote employees receiving a salary in home currency
- Small businesses paying international suppliers
- Expats investing in home country property
Now that you’ve chosen your payment app model, the next critical decision is deciding what features to actually build. Understanding the difference between essential and advanced features determines whether your app launches fast or gets stuck in development.
Build a Payment App With the Features Your Users Need
Our expert app developers can help you build a feature rich payment solution with smooth transactions, strong security, and impressive performance. Let us turn your feature list into a real working app.
Core & Advanced Features for Modern Payment Apps
Building a payment app means making tough choices about features when you create money transfer app solutions. Essential features get you to market. Advanced features build a competitive advantage. This section breaks down what to build first versus what to add later. Master essential features, then layer in advanced ones as you grow and gather user feedback.
Essential payment app features
Essential features are non-negotiable; they form the foundation of your app’s MVP. Users expect them from day one, and without them, your app won’t function properly or gain adoption.
Feature Description Why It’s Essential User Registration & Authentication Email, phone, or social login with password security Users need secure access to accounts Secure Digital Wallet Encrypted storage for funds or linked payment methods Core function of payment apps Money Sending/Receiving Core ability to transfer funds between users Primary function of the app Payment Method Linking Connect bank accounts, debit cards, and credit cards Users need funding sources Real-time Transaction Status Show pending, processing, and completed states Users need to know the payment progress Transaction History View past transactions with details Users need records for accounting Push Notifications Alert users of login attempts, payments received, and transfers sent Keep users informed instantly Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) SMS or authenticator app verification Prevent account hijacking and fraud Customer Support Chat/Email Basic support channel for user issues Users have problems and need help KYC Compliance Identity verification during signup Regulatory requirements for financial apps PCI DSS Compliance Secure handling of payment card data Legal and security requirements Transaction Receipts Digital receipts for every transaction Users need proof for record-keeping Advanced payment app features
Advanced features create a competitive advantage. They’re not essential for launch, but they drive user engagement, retention, and growth. Add these after your core users validate the essential features.
Feature Description Why It’s Needed Biometric Authentication Fingerprint or face recognition login Faster, secure login / Users prefer one-tap over passwords AI-Powered Fraud Detection Detects suspicious transactions using machine learning Prevents fraud / Users feel protected Social Features Notes, emojis, friend lists, activity feed Social transfers / Viral growth via network effects Recurring Payments Schedule automatic transfers Automate regular payments / Save time, reduce missed payments Bill Splitting Split expenses automatically Solve common problems / Share app with friends, splitting bills Spending Analytics Charts and insights on money flow Financial insights / Help understand money Cryptocurrency Support Send and receive crypto (BTC, ETH, stablecoins) Crypto-native users / Tap into the crypto payment market International Transfers Send money across borders Serve global users / Access untapped markets Subscription Management Manage subscriptions in one place Track subscriptions / Consolidate financial management Cashback & Rewards Rewards for transactions Incentivize use / Get value beyond basic service Invoice Creation Generate invoices for freelancers, SMBs Serve businesses / Expand use cases beyond personal payments API for Third Parties Let other apps integrate Ecosystem building / Revenue from partners Voice Commands Send money using voice Accessibility / Serve the elderly, accessible to all Loyalty Programs Points or rewards for frequent users Retention / Users stay loyal for rewards Smart Recommendations Suggest payments by history Personalize user experience / Discover features Real-time Notifications with AI Predictive alerts about unusual activity Catch fraud/errors early / Users feel in control Recommended feature launch strategy
- For Launch: Build the 12 essential features in the first table. These are your MVPs.
- For Iteration 2: Pick 3–4 advanced features your users ask for the most. Add those next.
- For Scale: Keep adding advanced features that align with your business model and user feedback.
Key Principle: Essential features are table stakes. Advanced features are competitive differentiators. Launch with excellence on essential features. Win market share with advanced features.
Now you know what to build. The question every founder asks next is: how much will it cost?
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Payment App?
The payment app development cost typically ranges from $40,000 to $300,000+, depending on your app’s complexity, security needs, compliance requirements, and the level of scalability you want. Since payment apps handle sensitive financial data and must meet strict regulatory standards, costs are generally higher than standard mobile apps.
Cost by Complexity Level
The most straightforward way to understand payment app development costs is by complexity tier. Each tier includes different features, platforms, and development timelines.
| Complexity Level | Cost Range | Timeline | What’s Included |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic MVP | $40,000–$80,000 | 3–4 months | Essential features only, basic security, single payment method |
| Mid-Level App | $80,000–$200,000 | 5–7 months | Most essential features, multiple payment methods, advanced security, and analytics |
| Enterprise-Level App | $200,000–$500,000+ | 8–12 months | All advanced features, AI fraud detection, API for partners, 24/7 support |
| Complex Payment Platform | $500,000–$2,000,000+ | 12–18+ months | Custom payment processing, blockchain support, global compliance, enterprise features |
Cost by Payment App Model
Different payment app models have different cost profiles. Some require more infrastructure investment than others.
| Model | Development Cost | Why It Costs More/Less |
|---|---|---|
| P2P Payment App | $80,000–$250,000 | Moderate infrastructure needs, heavy compliance |
| Merchant Payment App | $100,000–$300,000 | Requires payment processor relationships |
| Digital Wallet | $150,000–$500,000+ | Complex tokenization and card network integration |
| Payment Processing Platform | $300,000–$2,000,000+ | Highest infrastructure complexity |
| Foreign Exchange App | $100,000–$400,000 | Requires global banking relationships |
Key factors that influence the cost of payment app development
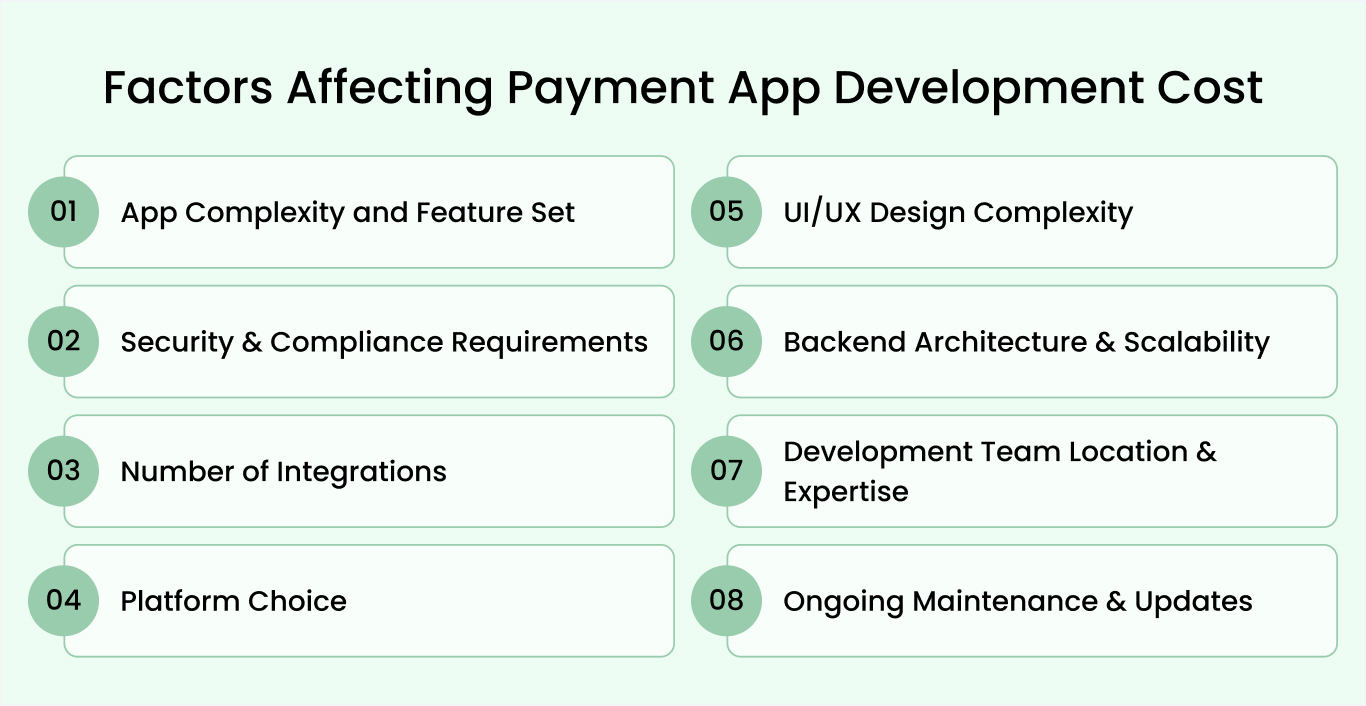
The cost of payment app development isn’t fixed; it varies widely based on your product vision, compliance needs, and the level of security you want to build. Here are the major factors that determine how much it costs to build a payment app:
App complexity and feature set
The more advanced your features, the higher the development cost. A simple P2P app with basic transfers and user profiles costs significantly less than an enterprise-grade solution with multi-currency support, instant settlements, and AI-powered fraud detection.
Security & compliance requirements (PCI-DSS, KYC/AML)
Payment apps run on trust, and security is non-negotiable. Building PCI-DSS–compliant architecture, integrating KYC/AML systems, encrypting sensitive data, adding tokenization, and conducting security audits all impact your budget.
Number of integrations
Integrations such as:
- Payment gateways
- Banking APIs
- Fraud detection engines
- Identity verification services
- Cryptocurrency rails (optional)
Each integration adds development time, testing effort, and cost.
Platform choice (iOS, Android, or Both)
Choosing to build for both iOS and Android naturally doubles development and QA efforts, unless you use cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native, which reduce cost and time.
UI/UX design complexity
Payment applications must deliver frictionless onboarding, clean flows, and instant user feedback. Custom animations, micro-interactions, dashboards, and multi-step payment experiences require more design hours, increasing overall cost.
Backend architecture & scalability
A robust backend with low latency, high transaction throughput, real-time syncing, and multi-tenant architecture costs more to build but ensures your app can scale to millions of users without crashing.
Development team location & expertise
Hiring in-house fintech developers and hiring fintech software developers from an offshore agency in a different region changes cost significantly.
- US/Western Europe teams charge the highest
- Eastern Europe is mid-range
- India/Southeast Asia offers cost-efficient, high-quality fintech engineering
Ongoing maintenance & updates
3
After launch, you still need to budget for:- Bug fixes
- New features
- Security patches
- Compliance updates
- Server and cloud costs
This typically amounts to 15–25% of the initial payment software development cost annually. To understand how these ongoing expenses fit into your overall cost projections and ROI calculations, check out our detailed fintech app development cost breakdown guide.
Get a Clear and Accurate Cost Estimate for Your Payment App
We help you calculate an accurate budget based on features, integrations, and security requirements. Contact Space O Technologies for a detailed project estimate tailored to your business needs.
Step-by-Step Payment App Development Process
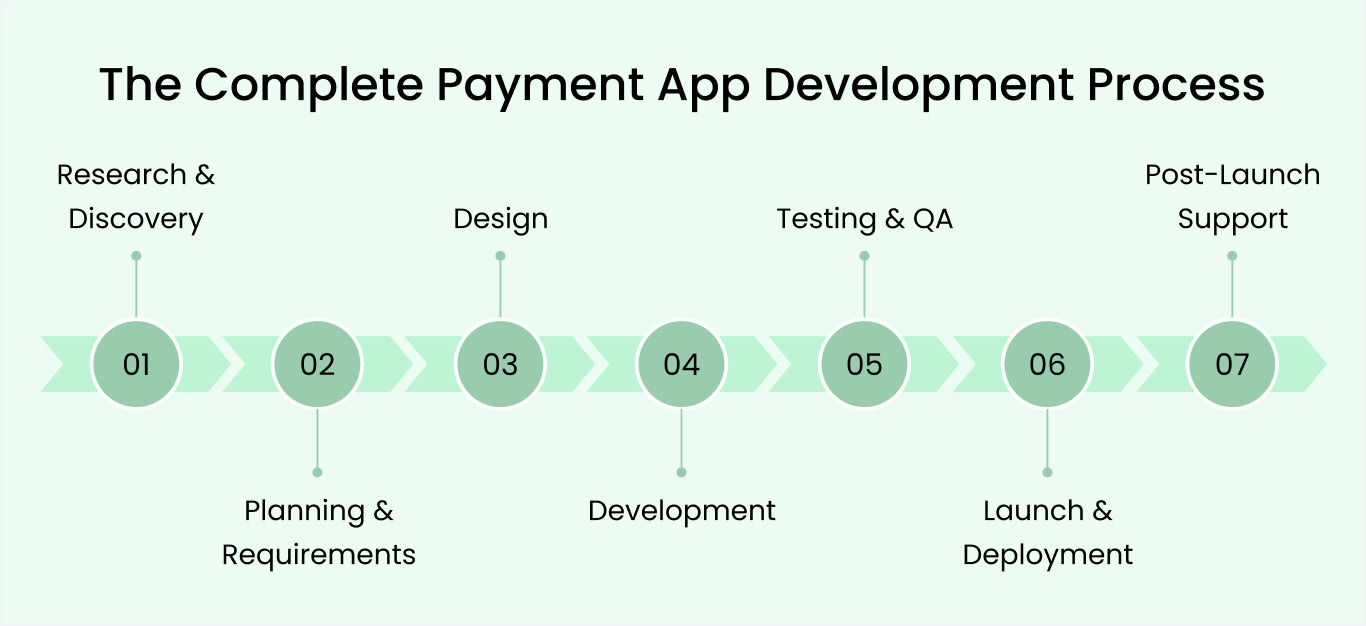
Building a payment app requires careful planning and systematic execution across multiple phases. Whether you’re creating your first mobile payment app or expanding existing financial services, following a structured fintech app development process ensures security, compliance, and market success from day one.
Phase 1: Research & discovery (2–3 weeks)
Every successful payment app starts with understanding your market, users, and regulatory landscape. This research phase determines whether your app idea solves real problems and identifies potential roadblocks before you invest heavily.
Key activities
- Conduct competitor analysis to understand what existing apps for mobile payment offer and where gaps exist
- Research user needs through surveys and interviews with your target audience
- Identify regulatory requirements for your target markets, as compliance affects every subsequent development decision
- Define your business model clearly, including revenue streams and growth projections
- Assess technical requirements and payment gateway options that align with your goals
Phase 2: Planning & requirements (1–2 weeks)
Transform research insights into concrete project specifications that guide development. This phase converts broad ideas into detailed technical blueprints that developers can execute without ambiguity.
What you’ll create
- Detailed functional requirements for every feature your app will include, from user registration to transaction processing
- User personas representing your primary customer segments
- Complete user journey maps showing how customers interact with your app
- Regulatory compliance roadmap outlining specific certifications needed and timelines for obtaining them
- Technical architecture, including databases, APIs, cloud infrastructure, and security protocols that will support your app at scale
Team Formation: Assemble your development team, whether in-house or partnering with a fintech software development company experienced in payment software development.
Phase 3: Design (2–4 weeks)
Design makes or breaks payment apps because users demand both security and simplicity. Great design reduces friction during transactions while building trust through visual clarity and professional polish.
Design deliverables:
- UX research findings showing how users interact with payment interfaces and what builds trust
- Wireframes displaying basic app structure and user flows without visual design elements
- Interactive prototypes that stakeholders can test before development begins
- Complete UI design with attention to accessibility, brand consistency, and platform guidelines for iOS and Android
- Detailed payment flows showing every step from transaction initiation to confirmation, including error states and edge cases
- Security architecture specifying encryption methods, authentication systems, and fraud detection mechanisms
Phase 4: Development (8–16 weeks)
This is where your payment app takes shape through code. Development consumes the most time and budget, but proper planning from earlier phases ensures efficient execution.
Backend development
- Build APIs, databases, and server infrastructure handling transactions securely.
- Integrate payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, or custom processors, depending on your business model and geographic scope.
- Implement security measures, including end-to-end encryption, secure authentication, and fraud detection systems from the foundation.
- Build compliance features like KYC verification, AML monitoring, and transaction reporting that regulators require.
Frontend development
- Create native iOS and Android apps or cross-platform solutions using React Native or Flutter for faster mobile payment app development.
- Connect frontend interfaces to backend APIs and payment processors.
- Implement user authentication, transaction interfaces, and account management features.
- Set up development and staging environments where you can test features safely before production deployment.
Phase 5: Testing & QA (2–4 weeks)
Payment apps handle money, so testing cannot be rushed or skipped. One security flaw or transaction bug can destroy user trust and expose you to significant financial and legal risks.
Testing types:
- Functional testing verifies every feature works correctly across devices and operating systems
- Security testing through penetration tests identifies vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit
- Load testing ensures your app handles peak transaction volumes without slowdowns or crashes
- Usability testing with real users reveals friction points that decrease conversions or create confusion
- Compliance verification confirms your app meets PCI DSS, KYC/AML, and regional data protection standards before launch
- Payment flow testing with small real transactions in sandbox environments provided by payment processors
Phase 6: Launch & deployment (1–2 weeks)
Prepare for launch systematically to avoid last-minute surprises. Rushing deployment creates vulnerabilities and operational problems that damage your reputation from day one.
Launch checklist:
- Submit apps to Apple App Store and Google Play Store (typically takes 1-7 days for approval)
- Configure production cloud infrastructure with proper security, monitoring, and backup systems active
- Implement continuous monitoring tools that alert you immediately when issues occur
- Execute your launch marketing strategy to drive initial user acquisition
- Start with a soft launch in limited markets to validate everything works correctly before broader rollout
- Activate customer support systems because users will have questions during onboarding
Phase 7: Post-launch support (Ongoing)
Launch day is just the beginning. Successful payment apps evolve continuously based on user feedback, security threats, and regulatory changes.
Ongoing activities
- Monitor app performance, transaction success rates, and user feedback continuously
- Fix bugs immediately because payment apps require high reliability
- Implement feature enhancements based on user requests and competitive analysis
- Update security measures as new threats emerge and maintain compliance as regulations evolve
Post-launch evolution is where most payment apps succeed or fail. For a deeper dive into managing each development phase, check out our guide on how to build a fintech app.
Understanding how to create a payment app through systematic process management sets you up for success, but security and compliance are the non-negotiable foundations that protect your business and users. Let’s take a deeper look at them.
Get Expert Assistance for Payment App Development
From planning to launch, we follow a structured and transparent development process that ensures secure and stable results.
Payment App Security & Compliance: Non-Negotiables
Security breaches and compliance failures ruin payment apps overnight. When you make a payment app, you’re handling real money; corners aren’t just risky, it’s business suicide. Building your security and compliance strategy from day one protects your customers, reduces risk, and ensures your app can scale safely.
Mandatory compliance requirements
Payment apps operate in a heavily regulated environment. Meeting compliance isn’t optional; it’s a legal requirement that comes with strict enforcement and severe penalties.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
If your app processes or stores card data, PCI DSS compliance is mandatory. It ensures secure network architecture, strong access control, continuous monitoring, and secure handling of cardholder information. Core requirements include:
- Strong network firewall management
- No default system passwords
- Encryption for stored and transmitted cardholder data
- Updated antivirus and vulnerability management
- Role-based access control
- Logging and monitoring
- Annual audits and quarterly scans
Non-compliance can cost $5,000–$100,000 per month. Any reputable payment app development company builds PCI compliance into the architecture from the start.
KYC/AML (Know Your Customer / Anti-Money Laundering)
Regulators require all payment apps to verify users and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Requirements vary across countries but generally include:
- Identity verification (ID, address, facial match, etc.)
- Screening against sanctions and PEP lists
- Real-time fraudulent behavior monitoring
- Mandatory suspicious activity reporting
- Record retention for 5–7 years
Failing KYC/AML can lead to regulatory action, criminal exposure, and irreversible reputation damage.
Data privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
These laws govern how user data is collected, stored, and used. Key obligations include:
- Obtaining explicit user consent
- Strong privacy notices
- User rights (access, download, delete)
- Data minimization
- 72-hour breach notifications
GDPR fines can reach €20 million or 4% of global revenue in the event of a breach.
OFAC compliance
For online payment transfer app development with international reach, OFAC screening prevents transactions with sanctioned individuals or countries. Violations include fines up to $20 million.
Security measures every payment app needs
Compliance sets a baseline, but modern payment apps require stronger, multi-layered security to defend against evolving threats.
End-to-end encryption
Encrypt all sensitive data at rest (AES-256) and in transit (TLS 1.3). Never store plain-text card data. Use secure key management systems like AWS KMS or HashiCorp Vault. Enable certificate pinning to block man-in-the-middle attacks.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are not enough. Implement SMS OTP, authenticator apps, biometrics, or hardware keys. Enforce MFA for high-risk actions like withdrawals and password resets.
Biometric authentication
Use native device APIs for fingerprint or facial recognition, fast, secure, and frictionless. Never store biometric data on your servers.
AI-powered fraud detection
Machine learning detects anomalies better than rule-based systems. Use ML models to analyze:
- Transaction velocity
- Location mismatches
- Withdrawals outside user patterns
- High-risk device fingerprints
- Flag suspicious actions before the transaction completes.
Secure API architecture
Use OAuth 2.0 or JWT, implement rate limiting, validate all requests, and avoid leaking system information in API responses. Use gateways for centralized logging, auth, and traffic control.
DDoS & infrastructure protection
Use cloud-native DDoS protection (AWS Shield, Cloudflare), auto-scaling, and intrusion detection. Follow least-privilege access and segment your network.
Regular penetration testing & security audits
Run quarterly pen tests, annual full audits, automated vulnerability scans, and maintain a patch schedule. Implement a responsible disclosure or bug bounty program to catch real-world exploits early.
Security and compliance form the foundation, but even well-secured payment apps face operational challenges during development and growth. Understanding these challenges before they occur helps you navigate them successfully.
Common Payment App Development Challenges (& Solutions)
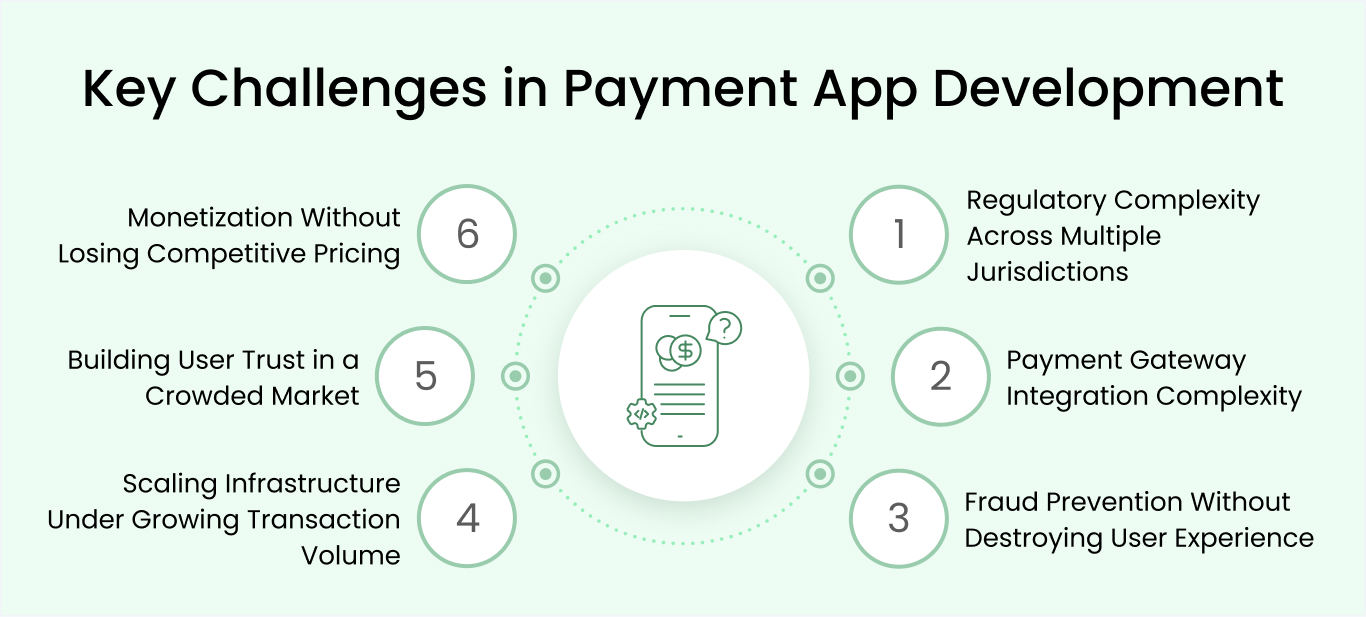
Even experienced development teams encounter obstacles when building payment apps. These challenges range from technical complexity to market positioning, but each has proven solutions that successful apps have implemented. Understanding these roadblocks before you start helps you navigate them efficiently.
Challenge 1: Regulatory complexity across multiple jurisdictions
Payment regulations vary dramatically by country and region, creating compliance nightmares for apps serving international users. Each market requires different licenses, KYC procedures, and reporting standards. Navigating this complexity without legal expertise causes costly delays and potential regulatory violations.
Solutions
- Partner with compliance experts and legal counsel specializing in fintech regulations from day one
- Build compliance into your app’s foundation rather than retrofitting later
- Start with one market to master regulations before expanding geographically
- Use compliance-as-a-service platforms like Onfido or Jumio that handle KYC/AML verification
- Budget 10-15% of total development costs for compliance implementation and ongoing maintenance
Challenge 2: Payment gateway integration complexity
Integrating multiple payment processors, each with different APIs, authentication methods, and data formats, creates technical challenges. Payment gateways handle sensitive financial data requiring perfect implementation. Integration errors cause transaction failures that destroy user trust and generate support nightmares.
Solutions
- Use payment aggregators like Stripe or PayPal that provide unified APIs supporting multiple payment methods
- Build an abstraction layer separating your app logic from specific gateway implementations
- Test payment integrations extensively in sandbox environments before going live
- Implement comprehensive error handling for every possible gateway response
- Maintain relationships with multiple payment processors to avoid single points of failure
Challenge 3: Fraud prevention without destroying user experience
Balancing security with convenience remains the eternal payment app challenge. Aggressive fraud prevention creates friction that drives users away. Lax security invites fraud that costs money and damages reputation. Fraudsters constantly evolve tactics, making static security measures ineffective over time.
Solutions
- Implement AI-powered fraud detection that learns user patterns and identifies anomalies
- Use risk-based authentication requiring additional verification only for suspicious transactions
- Monitor for fraud indicators like rapid transaction sequences, unusual amounts, or geographic anomalies
- Use device fingerprinting to detect suspicious device changes or emulators
- Provide clear communication when blocking transactions so legitimate users understand why
Challenge 4: Scaling infrastructure under growing transaction volume
Payment apps experience explosive growth when they gain traction, overwhelming infrastructure not built for scale. Database bottlenecks cause slow transactions. Server failures during peak usage create outages. Poor architecture decisions early in development require expensive rewrites when scaling becomes critical.
Solutions
- Build on cloud infrastructure supporting auto-scaling from day one
- Use a microservices architecture that allows scaling individual components independently
- Conduct load testing simulating 10x your expected peak transaction volume
- Implement database sharding and caching strategically to reduce bottlenecks
- Monitor performance metrics continuously and optimize bottlenecks before they cause problems
Challenge 5: Building user trust in a crowded market
New payment apps face skepticism from users hesitant to trust another platform with their money. Established competitors like PayPal and Venmo have massive user bases and brand recognition. Overcoming this trust barrier requires more than just features; it demands strategic positioning and credibility building.
Solutions
- Display security certifications and compliance badges prominently throughout your app
- Partner with established financial institutions, lending credibility to your platform
- Start with a defined niche market rather than competing broadly against giants
- Collect and showcase user testimonials and case studies demonstrating reliability
- Implement transparent fee structures without hidden charges and provide responsive customer support
Challenge 6: Monetization without losing competitive pricing
Finding sustainable revenue models while keeping prices competitive enough to attract users creates constant tension. Transaction fees must cover operational costs, compliance expenses, and generate profit margins. Setting fees too high drives users to competitors, while pricing too low makes profitability impossible.
Solutions
- Implement multiple revenue streams rather than relying solely on transaction fees
- Offer tiered pricing with free basic features and premium paid options
- Create B2B services (APIs, white-label solutions), generating revenue from businesses
- Negotiate volume discounts with payment processors as you scale
- Use data analytics to identify which features justify premium pricing
These challenges are significant but not insurmountable. Understanding how to create a mobile payment app successfully means anticipating these obstacles and implementing proven solutions from the start.
Build Your Payment App With Space-O Technologies
Creating a successful payment app means understanding market dynamics, selecting appropriate business models, integrating critical features, and managing intricate security and compliance frameworks. From budget planning and development workflows to addressing operational obstacles, each choice affects your platform’s safety, growth potential, and competitive positioning.
This is where Space-O Technologies excels. With 15+ years delivering custom software solutions for 1,200+ clients worldwide, we’ve partnered with fintech startups, established enterprises, and payment service providers to launch secure, high-performing digital payment platforms.
We build PCI DSS-certified, KYC/AML-compliant, and highly reliable payment applications that enable seamless transactions and strengthen user trust. These apps adhere to regulatory requirements and are designed to scale with your business as technology and market demands evolve.
Whether you need to build a personal finance app, P2P app, merchant payments platform, or feature-rich digital wallet, our team guides you through the entire development lifecycle. This covers concept validation, UI/UX design, secure engineering, compliance integration, and ongoing product maintenance. Check our portfolio to know more:
Ready to transform your payment app vision into a secure, modern digital solution? Get a free consultation with our fintech experts today and start building a platform that drives real business results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Payment App Development
How much does it cost to develop a payment app?
Payment app development services cost $40,000–$500,000+, depending on complexity. Basic MVPs require $40,000–$80,000 over 3–4 months. Mid-level apps cost $80,000–$200,000 in 5–7 months. Enterprise platforms need $200,000–$500,000+, requiring 8–12 months.
Hidden costs include cloud hosting, PCI DSS compliance, KYC/AML verification, payment gateway fees, and maintenance, consuming 15–20% of initial development costs annually.
How long does it take to build a payment app?
Development timelines vary by complexity. Basic MVPs take 3–4 months, mid-level apps require 5–7 months, and enterprise platforms need 8–12 months. Complex payment processing systems take 12–18+ months. Agile methodology delivers features incrementally.
Timelines depend on feature scope, compliance requirements, and team experience. Cross-platform development using React Native or Flutter reduces time by 30–40% compared to native development.
How do payment apps make money?
Payment apps generate revenue through multiple streams. Transaction fees, typically 1–3%, provide the primary income, while interchange fees from card networks add additional revenue. Premium subscriptions offer advanced features, and business services such as API access create B2B revenue.
Apps can also earn passive income from interest on held balances. Successful apps diversify their revenue streams rather than relying solely on transaction fees. For more monetization strategies specific to different fintech models, check out our guide on how do fintech apps make money.
What programming languages are best for payment app development?
The best programming languages for payment app development depend on platform and requirements. Swift ensures native iOS security, while Kotlin provides modern Android features. Cross-platform frameworks like React Native and Flutter reduce development time by 30–40%. For the backend, use Node.js for scalability, Python for AI, or Java for enterprise systems.
How do I ensure my payment app is secure?
Ensuring your payment app is secure requires multiple layers of protection. Implement AES-256 encryption for data storage and TLS 1.3 for transmission, and use multi-factor authentication combining passwords, biometrics, and device verification.
Deploy AI-powered fraud detection, maintain PCI DSS compliance, and implement KYC/AML verification. Conduct quarterly security audits and penetration testing, and secure all APIs using OAuth 2.0 authentication with rate limiting.
Do I need to integrate with multiple payment gateways?
Multiple gateways provide flexibility, redundancy, and broader payment support. They prevent single points of failure and offer better rates for specific regions. However, each adds complexity and costs. For MVPs, start with one aggregator like Stripe or PayPal. As you scale, add specialized gateways for international payments or cryptocurrency based on actual user demand.