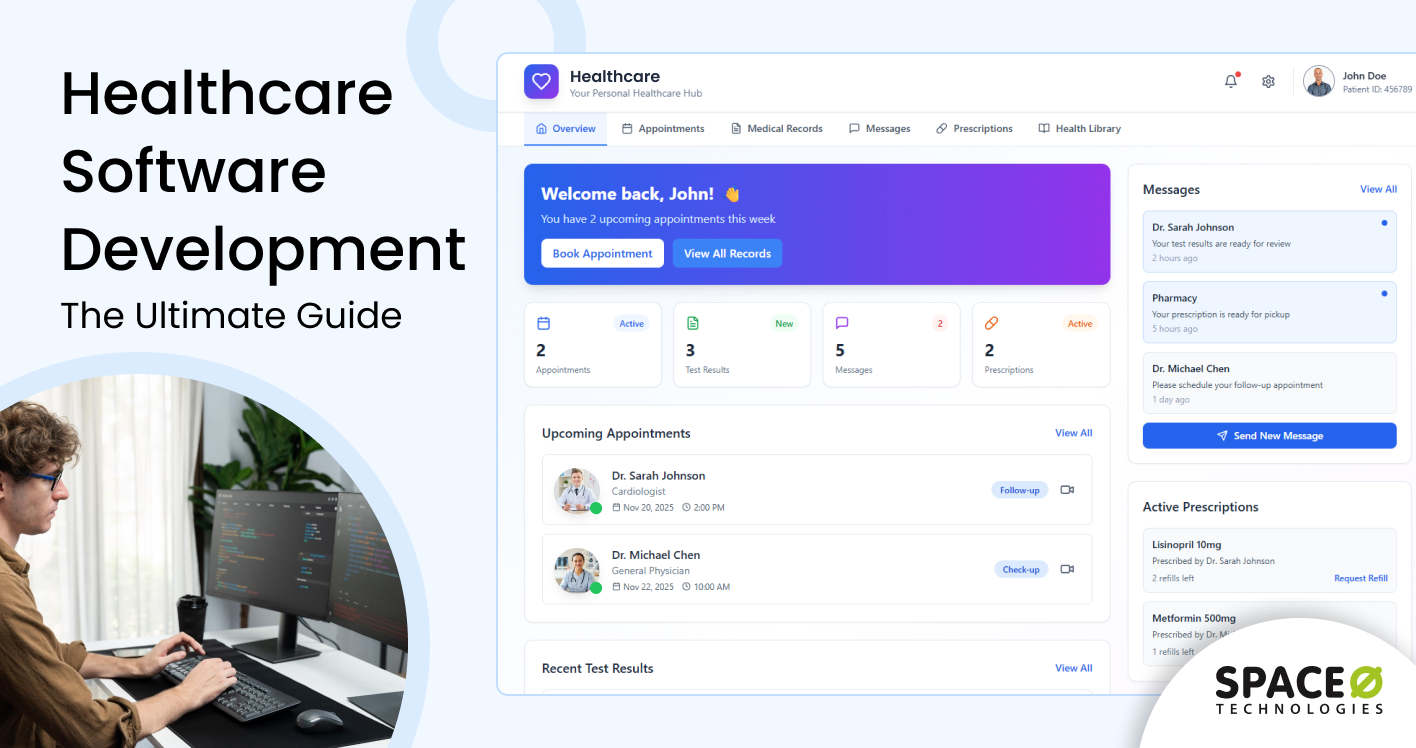
In today’s fast-changing healthcare world, technology is becoming the backbone of efficient, patient-focused care. Healthcare software development is all about creating custom digital solutions that make clinical workflows smoother, engage patients more effectively, and ensure strict compliance with healthcare regulations.
The demand for digital healthcare solutions is skyrocketing. As per Grand View Research, the digital healthcare market was valued at USD 288.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 946.04 billion by 2030.
Many healthcare organizations still rely on manual processes or outdated systems, which can slow things down and affect patient outcomes. By embracing purpose-built software, healthcare providers can streamline operations, deliver better patient experiences, and improve care quality, all while staying fully compliant with regulations.
This blog is your ultimate guide to developing healthcare software, based on our experience as a leading healthcare software development company. Explore the different types of healthcare software, essential features, the development process, and how custom solutions can help healthcare organizations overcome challenges and deliver safer and more efficient care.
Table of Contents
What is Healthcare Software Development?
Healthcare software development is the process of designing, building, and maintaining digital solutions specifically for the healthcare industry. It involves creating applications and platforms that help healthcare providers, patients, and administrators manage clinical, administrative, and operational tasks more efficiently.
These solutions can range from electronic health records (EHR) and patient management systems to telehealth apps, mobile health tools, and AI-powered analytics platforms. The goal is not just digitization, but smarter workflows, improved patient care, better data management, and enhanced decision-making.
In short, healthcare software development is about leveraging technology to make healthcare delivery safer, faster, and more effective, while also addressing the specific challenges of the industry, such as data privacy, interoperability, and user adoption.
Off-the-shelf healthcare software solutions vs. Custom software development
Healthcare organizations face a crucial choice when implementing software: adopt a ready-to-use solution or build a custom platform. This decision impacts how well the software fits existing workflows, scales with growth, and meets patient and provider needs.
| Aspect | Off-the-Shelf Software | Custom Healthcare Software |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ready-made solutions for a broad range of healthcare providers | Tailored software built to meet an organization’s specific requirements |
| Deployment Time | Faster deployment | Longer development time |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs | Higher initial investment |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility | Fully customizable to workflows and processes |
| Integration | May not integrate deeply with clinical workflows | Full alignment with existing workflows |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable to grow with the organization |
| Competitive Advantage | General-purpose, minimal differentiation | Can provide a competitive advantage through tailored features and functionality |
Choosing between off-the-shelf and custom solutions depends on your organization’s unique needs, workflows, and long-term goals. Overall, custom healthcare software development offers greater benefits in the long run. Such solutions are tailored to your unique organizational workflows and work according to your processes.
Understanding these options is crucial before understanding the different types of healthcare software solutions you can develop.
8 Key Types of Healthcare Software Solutions
The healthcare software ecosystem encompasses diverse applications serving different needs around patient care. Understanding these categories helps you identify which solutions align with your organizational goals.
Electronic health records (EHR) and Electronic medical records (EMR)
EHR and EMR systems form the digital backbone of modern healthcare facilities. These platforms centralize patient information, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization records, allergies, and lab results in one accessible location.
Key difference: EMRs contain patient data within a single practice, while EHRs share information across multiple healthcare organizations.
- Clinical documentation and note-taking
- Prescription management and e-prescribing
- Lab integration and results tracking
- Care coordination across departments
- Patient history and timeline views
Key capabilities:
Comprehensive EHR systems enable care coordination between primary care physicians, specialists, hospitals, and pharmacies, reducing duplicate tests and medication errors.
Hospital Management Systems (HMS)
Hospital management systems orchestrate complex multi-department operations across entire healthcare facilities. These enterprise platforms give you complete visibility into hospital operations from patient flow to financial performance.
- Patient admissions and discharges
- Bed allocation and tracking
- Staff scheduling and payroll
- Inventory control for medical supplies
- Billing and insurance claims
- Operational reports for administrators
Key capabilities:
For multi-facility healthcare networks, HMS platforms provide centralized visibility into operations, resource utilization, and financial performance across all locations, which is why organizations develop medical billing software solutions integrated within these systems.
Telemedicine and telehealth platforms
Telemedicine software enables remote healthcare delivery, extending your reach beyond physical clinic walls. These platforms became essential during the COVID-19 pandemic and continue growing as patients demand convenient access to care.
- Secure video consultations
- Real-time messaging between patients and providers
- Remote patient monitoring using connected devices
- Electronic prescription transmission
- Integrated appointment scheduling with payment processing
Key capabilities:
Today, these platforms serve rural areas with limited healthcare access, provide after-hours urgent care, and offer specialized consultations without geographic barriers. Develop your telemedicine solution with experienced healthcare software partners.
Patient portal solutions
Patient portals empower individuals to take active roles in their healthcare. These self-service platforms improve patient engagement while reducing administrative burden on your staff.
- View medical records and test results
- Schedule and manage appointments
- Communicate securely with care teams
- Request prescription refills
- Access educational materials about their conditions
Key capabilities:
Well-designed patient portals reduce administrative burden on staff while improving patient satisfaction and engagement scores.
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) and medical billing
Healthcare software solutions for revenue cycle management automate the complex financial operations of medical practices. These systems streamline your entire billing process from patient registration to final payment.
- Insurance eligibility verification
- Automated claims submission to payers
- Payment status tracking and follow-up
- Denial management and resubmission
- Patient billing and payment collection
- Compliance with ICD-10, CPT, and insurance regulations
Key capabilities:
Effective RCM software accelerates reimbursements, reduces claim denials, and improves cash flow for healthcare organizations.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS platforms leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to assist clinicians with complex diagnostic and treatment decisions. These intelligent systems augment clinical expertise with data-driven insights.
- Analyze patient data against vast medical knowledge bases
- Provide evidence-based treatment recommendations
- Identify potential drug interactions and contraindications
- Alert clinicians to critical lab values or vital signs
- Support diagnosis of rare or complex conditions
Key capabilities:
By combining clinical expertise with AI-powered analysis, CDSS improves diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS)
LIMS solutions streamline laboratory operations from specimen collection to result delivery. These systems ensure accuracy, efficiency, and compliance in clinical and research laboratories.
- Track specimens from collection through analysis
- Manage test orders and workflows
- Record and validate results
- Ensure quality control protocols
- Integrate with diagnostic equipment and analyzers
Key capabilities:
These systems reduce turnaround times, minimize errors, and maintain regulatory compliance for clinical and research laboratories.
Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications
Mobile health apps extend healthcare beyond clinical settings directly into patients’ daily lives. These applications keep patients engaged with their health between clinic visits.
- Medication adherence through reminders
- Chronic disease management and symptom tracking
- Fitness and wellness monitoring
- Integration with wearable devices and sensors
- Educational content delivery
Key capabilities:
mHealth apps are particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension that require continuous monitoring and lifestyle modifications.
Each type of healthcare software addresses specific operational challenges and patient needs. Many organizations implement integrated ecosystems combining multiple solutions for comprehensive digital health capabilities.
Looking to innovate? Our guide to top healthcare app ideas showcases solutions that enhance patient engagement and operational efficiency.
Understanding these solution types is just the first step. Next, let’s examine the tangible benefits that drive healthcare organizations to invest in custom software development for healthcare.
Turn Your Healthcare Software Idea Into a Working Product
Leverage our 15+ years of experience and proven expertise across 300+ software products to bring your healthcare solution to life.

Key Benefits of Healthcare Software Development
Healthcare software development transforms how medical organizations operate and deliver care. Whether you’re implementing custom solutions or adopting specialized platforms, modern healthcare software solutions deliver measurable advantages across clinical and administrative functions.
Improve patient care and outcomes
Healthcare software puts complete patient information at clinicians’ fingertips instantly. When doctors access comprehensive medical histories, medication lists, allergy information, and recent test results in seconds rather than minutes, they make faster, more accurate diagnostic decisions.
- Instant access to complete patient information enables faster diagnoses
- Seamless information flow between departments eliminates communication gaps
- Care coordination improves when all providers work from the same real-time data
- Reduced medical errors from incomplete or inaccurate information
- Better health outcomes through comprehensive, coordinated care
Key advantages
Enhances operational efficiency
Healthcare facilities waste countless hours on manual, repetitive administrative tasks. Healthcare software automates appointment scheduling, insurance verification, claims processing, and documentation workflows that previously consumed staff time.
- Process more patients without increasing staff size
- Reduce administrative costs substantially through automation
- Free clinical staff to focus on patient care rather than paperwork
- Eliminate time-consuming manual data entry across systems
- Improve staff satisfaction by removing tedious tasks
Key advantages
Improves data management and analytics
Modern healthcare systems centralize fragmented data from multiple sources into unified platforms. Real-time dashboards provide actionable insights into patient populations, treatment effectiveness, resource utilization, and operational bottlenecks.
- Centralized data from multiple sources in one unified platform
- Real-time dashboards showing actionable insights
- Track metrics that matter to your organization
- Predictive analytics identify at-risk patients before conditions deteriorate
- Data-driven decisions based on your organization’s actual performance
Key advantages
Enhances regulatory compliance and security
Modern healthcare software development prioritizes compliance and security from the ground up. Well-designed systems meet HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH requirements as foundational design principles, not afterthoughts.
- HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH compliance built in from the foundation
- Multi-layered security controls protecting sensitive patient data
- Encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails
- Comprehensive documentation demonstrating compliance during audits
- Regular updates, maintaining compliance as regulations evolve
Key advantages
Ensures Scalability and flexibility
Quality healthcare software grows with your organization. Adding new locations, expanding services, or increasing patient volumes becomes manageable without complete system overhauls that disrupt operations.
- Scale to accommodate organizational growth
- Cloud-based architectures adjust computing resources automatically
- Adapt workflows as your organization’s needs evolve
- Support multi-location operations from centralized platforms
- Handle increasing data volumes without performance degradation
Key advantages
Increases cost-effectiveness over time
While healthcare software requires investment, organizations realize substantial returns through improved efficiency, reduced errors, and better patient outcomes. The benefits compound over time as staff become proficient and workflows are optimized.
- Reduce operational costs through automation and efficiency
- Minimize errors that lead to costly corrections and liability
- Improve patient retention through better experiences
- Recover investment through improved operations
- Increase revenue capacity without proportional cost increases
Key advantages
These benefits explain why healthcare organizations, from small practices to large hospital networks, prioritize healthcare software development as a strategic investment in their future.
With clear benefits established, let’s examine the essential features that make healthcare software effective and the advanced capabilities that create competitive advantages.
Start Your Custom Healthcare Software Project With Experts
Work with our seasoned healthcare developers to create intuitive, secure, and future-ready software for your organization.
Essential Features of Healthcare Software
Building effective healthcare software requires balancing comprehensive functionality with intuitive usability. Here’s what your healthcare software should include to deliver real value.
Core features (Must-haves)
Every healthcare application needs these foundational capabilities regardless of the specific use cases. Here are the must-have features for developing healthcare software:
1.1 User authentication and role-based access
Ensures only authorized personnel view sensitive information. Different staff members access only data and functions relevant to their roles.
1.2 Patient data management
Centralizes demographics, medical history, medications, allergies, and immunization records in structured formats, eliminating information gaps.
1.3 Appointment scheduling
Enables efficient calendar management for providers and facilities. Automated reminders reduce no-shows while online scheduling improves convenience.
1.4 Electronic prescribing (e-Prescribing)
Transmits prescriptions directly to pharmacies electronically, reducing errors while automatically checking drug interactions and insurance formulary compliance.
1.5 Billing and invoicing
Handles complex healthcare payment scenarios, including insurance claims, patient balances, payment plans, and multiple payer sources.
1.6 Reporting and analytics
Generates insights into clinical outcomes, operational performance, financial metrics, and regulatory compliance through customizable dashboards.
1.7 Document management
Securely stores and retrieves consent forms, insurance cards, referral letters, and medical images with version control for audit trails.
1.8 Interoperability through HL7 and FHIR
Enables standardized data exchange with external systems, ensuring effective communication within the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Advanced features (Competitive advantages)
Beyond core functionality, these sophisticated capabilities differentiate exceptional healthcare software solutions from basic implementations.
2.1 AI and machine learning
Analyzes patient data to assist diagnoses, predict health risks, recommend treatments, and identify patterns across populations. Natural language processing extracts structured data from clinical notes.
2.2 Blockchain technology
Provides immutable audit trails for data access, secures pharmaceutical supply chains, and enables patients to control access to medical records.
2.3 IoT integration
Connects wearable devices, remote monitoring equipment, and smart hospital systems to track vital signs and disease progression continuously.
2.4 Voice recognition
Enables hands-free clinical documentation through dictation, reducing screen time and improving accessibility for users with mobility limitations.
2.5 AI chatbots
Handle routine patient inquiries 24/7 about appointments, symptoms, medications, and clinic information, escalating complex issues to human staff.
2.6 Telemedicine capabilities
Integrate video consultations, digital prescriptions, and remote monitoring into unified platforms, extending healthcare delivery beyond physical locations.
2.7 Mobile accessibility
Ensures clinicians access patient information from smartphones and tablets, supporting care delivery at the point of service.
Security features (Non-negotiables)
Healthcare software security cannot be an afterthought. These protections must be architectural foundations. Here are essential features to improve your healthcare software’s security:
3.1 End-to-end encryption
Protects data in transit and at rest using AES-256 encryption, ensuring intercepted data remains unreadable without decryption keys.
3.2 Multi-factor authentication
Requires multiple verification methods: passwords plus biometrics, security tokens, or one-time codes, preventing unauthorized access.
3.3 Data backup and disaster recovery
Automatically replicates data to multiple geographic locations with tested recovery procedures, ensuring rapid restoration if systems fail.
3.4 Audit logs and compliance tracking
Records every data access, modification, and transmission with timestamps and user identification, demonstrating regulatory compliance.
3.5 Role-based permissions
Granularly controls which users can view, edit, or delete specific data types, limiting exposure to the minimum necessary for each role.
3.6 Secure API integration
Protects data exchanges with third-party systems through authentication tokens, encryption, and rate limiting, preventing abuse.
Balancing comprehensive features with intuitive design requires experienced healthcare software developers who deeply understand clinical workflows. The right feature set depends on your specific use cases, user populations, and organizational goals.
With features defined, let’s walk through the systematic process that transforms requirements into functional healthcare software.
Healthcare Software Development Process
Successful healthcare software development follows a structured, proven methodology that ensures quality, compliance, and user satisfaction. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the software development process to build a healthcare solution.
Step 1: Discovery and requirement analysis
Every project starts with a deep understanding of your organizational goals, challenges, and users. This step involves stakeholder workshops with doctors, nurses, administrators, and IT staff to document requirements from every angle.
- What happens here: Workflow mapping identifies bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in your existing processes.`
- Outcome: A clear, compliance-ready roadmap that guides design and development, and defines success criteria.
Step 2: Planning and strategy
Once requirements are established, teams move to strategic planning. This stage defines the technology stack, system architecture, compliance roadmap, and development milestones.
- What happens here: Teams balance innovation with reliability, ensuring technologies meet healthcare’s demands for scalability, interoperability, and fault tolerance.
- Outcome: A detailed, realistic plan that ensures alignment between business goals and technical execution.
Step 3: UI/UX design
At the heart of successful healthcare software solutions development lies intuitive design. It needs to ensure that both clinicians and patients can navigate systems easily, regardless of their technical skills.
- What happens here: Designers conduct user research, create personas, and build interactive prototypes that simulate real-world usage.
- Outcome: Interfaces that simplify complex workflows, improve accessibility, and minimize training time.
Step 4: Development
In this phase, developers begin building the application using agile methodologies, typically in two-week sprints. For this stage, partnering with an expert software development company like Space-O Technologies can be a good idea.
Outsourcing healthcare software development requirements to such agencies helps build a healthcare software solution without excessive investment in a software development team, infrastructure, and technologies.
- What happens here: Each sprint delivers functional modules for early testing and feedback. Code reviews maintain consistency and quality across the project.
- Outcome: Secure, scalable software built with robust APIs following standards like HL7 FHIR for smooth integration across platforms.
Step 5: Quality assurance and testing
Custom medical software development requires rigorous, multi-dimensional testing before deployment. Each module is carefully validated to ensure reliability, interoperability, and compliance with strict healthcare standards before it reaches end users.
- What happens here: Functional, performance, and security testing validate that the system operates flawlessly under real conditions. Penetration and vulnerability testing ensure data safety.
- Outcome: A reliable, HIPAA-compliant system with strong data protection and performance under peak load.
Step 6: Deployment
The deployment stage introduces the software into live healthcare environments with minimal disruption.
- What happens here: Teams execute a staged rollout, beginning with smaller user groups before full-scale adoption. Server configurations and monitoring systems ensure performance and uptime.
- Outcome: Smooth transition from development to production with continuous tracking of performance and security metrics.
Step 7: Maintenance and support
Post-launch software development services for healthcare ensure ongoing system reliability, compliance, and scalability. Continuous monitoring and regular updates keep the software optimized for performance while adapting to evolving clinical, regulatory, and user requirements. You can either hire in-house software developers or partner with a software maintenance service provider to keep your healthcare platform up and running.
- What happens here: Teams provide 24/7 monitoring, regular security patches, performance optimization, and feature updates.
- Outcome: A continuously improved, secure, and regulation-compliant system that adapts to changing patient and provider needs.
This proven process ensures health software development projects deliver solutions that meet requirements, delight users, and achieve business objectives.
Understanding the development process is crucial, but building healthcare software also requires certain investment. Let’s understand how much it costs to develop healthcare software solutions.
Let Our Team Handle Your Entire Software Development Journey
From planning to deployment, Space-O Technologies delivers healthcare software with proven processes and deep industry experience.
Healthcare Software Development Cost Breakdown
Understanding the financial investment required for healthcare software development helps you plan budgets realistically and make informed decisions. Software development costs vary significantly based on project complexity, features, integrations, and compliance requirements.
Here’s a quick breakdown of estimated costs, timelines, and ideal use cases based on software complexity:
| Complexity Level | Cost Range | Timeline | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | $40,000–$80,000 | 3–5 months | Patient portals, appointment scheduling, and basic telemedicine |
| Mid-Level | $80,000–$200,000 | 6–9 months | Practice management systems, integrated EHR, and advanced telemedicine |
| Enterprise | $200,000–$500,000+ | 10–18 months | Hospital management systems, multi-facility EHR, and AI-powered platforms |
Basic Healthcare Software ($40,000–$80,000)
Simple solutions like patient portals, appointment scheduling systems, or basic telemedicine platforms fall into this category. Development typically takes 3–5 months.
- User registration and authentication
- Basic patient information management
- Appointment booking and reminders
- Simple reporting capabilities
- Single platform deployment (iOS or Android)
What’s included:
Mid-Level Healthcare Software ($80,000–$200,000)
Comprehensive practice management systems, integrated EHR solutions, or advanced telemedicine platforms require mid-level investment. Development spans 6-9 months.
- Cross-platform deployment (iOS and Android)
- HIPAA-compliant architecture and security
- Integration with existing healthcare systems
- Advanced features like e-prescribing and billing
- Pharmacy and delivery partner management panels
- Real-time analytics dashboards
What’s included:
Enterprise Healthcare Software ($200,000–$500,000+)
Large-scale hospital management systems, multi-facility EHR platforms, or AI-powered clinical decision support systems demand enterprise-level investment. These complex projects take 10–18 months.
- AI and machine learning capabilities
- Blockchain for enhanced security
- IoT integration for remote monitoring
- Telemedicine with advanced features
- Comprehensive interoperability (HL7 FHIR)
- Multi-location and multi-department support
- Advanced analytics and reporting
What’s included:
A clear understanding of development costs is just one part of the picture, because building healthcare software isn’t only about features and functionality. It also requires meeting strict industry regulations, which brings us to the next critical aspect: healthcare software compliance and regulations.
Get a Clear, Personalized Healthcare Software Development Cost Estimate
Share your project requirements, and we will guide you with an accurate, transparent cost breakdown tailored to your goals.
Healthcare Software Compliance and Regulations
Regulatory compliance is a legal requirement in healthcare software development, with serious penalties for violations. Building compliance from day one protects your organization, patients, and investment. Whether you work with a custom healthcare software development company or develop in-house, it must remain a core priority.
HIPAA (United States)
In the U.S., HIPAA is the cornerstone of healthcare data privacy and security, governing how patient information is handled and protected. It is made up of:
- Privacy Rule: Restricts who can access protected health information (PHI). Patients must authorize disclosure except for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations. Software must enforce restrictions through role-based permissions.
- Security Rule: Requires administrative, physical, and technical safeguards protecting electronic PHI. Administrative safeguards include security policies and staff training. Physical safeguards control facility access. Technical safeguards encompass access controls, encryption, and audit logging.
- Breach Notification: Requires notifying affected individuals, HHS, and potentially the media within specific timeframes when PHI is compromised. Comprehensive audit trails demonstrate compliance during investigations.
HITECH Act
The HITECH Act expands HIPAA’s (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) reach, reinforcing compliance accountability and encouraging the use of electronic health records (EHRs).
It strengthens HIPAA enforcement, promotes EHR adoption, increases penalties for violations, and extends compliance obligations directly to business associates, including healthcare software development companies and cloud providers in the USA.
GDPR (European Union)
The GDPR sets the gold standard for data protection and privacy across the EU, demanding transparency and patient control over their data. It contains:
- Explicit Consent: Required for data collection and processing. Patients must actively agree through clear affirmative action, not pre-checked boxes.
- Individual Rights: Grants extensive rights to access, correct, delete, and port personal data.
- Breach Notification: Must occur within 72 hours of discovery, ensuring timely communication with regulators and affected individuals to maintain transparency and accountability.
- Data Minimization: Requires collecting only information necessary for specified purposes without “nice to have” data.
FDA Regulations
Health Level Seven (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) are global standards that enable secure and seamless data exchange between healthcare systems.
While not legal requirements, these standards enable critical data exchange between healthcare systems. Modern healthcare software product development must support these protocols for effective ecosystem integration.
Other regional regulations
- PIPEDA (Canada): Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act
- Australian Privacy Principles: Data protection requirements
- NHS Digital Standards (UK): National Health Service requirements
Compliance is ongoing, not one-time. Regulations evolve, vulnerabilities emerge, and software requires continuous monitoring and updates. Partner with experienced healthcare solution development services providers to build compliance into foundations rather than retrofitting later.
Security and compliance form the foundation, but even well-designed, compliant software faces operational challenges during development and launch. Let’s examine the most common hurdles and proven solutions.
Challenges in Healthcare Software Development (and Solutions)
Even well-planned projects face obstacles. Here are the most common challenges in healthcare software development and proven solutions to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Data security and privacy
Problem
Healthcare data represents valuable targets for cybercriminals. Breaches expose sensitive information, trigger regulatory penalties, damage reputation, and undermine patient trust. Hackers constantly evolve attack methods through ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits.
Solutions
- Implement defense-in-depth security with multiple overlapping protections
- Use end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest
- Require multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access
- Conduct regular penetration testing, identifying vulnerabilities
- Build security as an architectural foundation, not an added feature
Challenge 2: Regulatory compliance complexity
Problem
Healthcare regulations are complex, constantly evolving, and vary by jurisdiction. HIPAA encompasses thousands of pages. International operations multiply complexity through GDPR and regional laws. Misunderstanding requirements leads to expensive retrofits, delayed launches, or legal penalties.
Solutions
- Engage healthcare compliance experts from project inception
- Build regulatory requirements directly into architecture
- Document everything meticulously, demonstrating due diligence
- Choose custom healthcare software development companies with proven compliance experience
- Verify certifications like ISO 27001
Challenge 3: System integration complexity
Problem
Healthcare facilities operate dozens of disparate systems (EHRs, billing platforms, laboratory equipment, imaging, pharmacy management) requiring seamless communication. Legacy systems use proprietary protocols, incomplete documentation, and outdated technologies. Failed integrations create dangerous information silos and duplicate data entry.
Solutions
- Use industry-standard protocols like HL7 FHIR for interoperability
- Build robust APIs with comprehensive error handling and monitoring
- Plan phased migration strategies for legacy systems
- Avoid risky “big bang” replacements
- Budget adequate time and resources (integration takes longer than anticipated)
Challenge 4: User Adoption Resistance
Problem
Healthcare professionals resist new software for legitimate reasons (overwhelmed with documentation requirements, skeptical after previous failed implementations, and focused primarily on patient care rather than learning systems). Poor adoption rates waste development investment and prevent the realization of expected benefits.
Solutions
- Involve end users throughout design, not just at the end
- Conduct user research, understanding actual workflows
- Design intuitive interfaces requiring minimal training
- Implement gradual rollouts with comprehensive training
- Provide on-site support during transitions
- Celebrate early adopters and address concerns transparently
Challenge 5: Balancing features and usability
Problem
Healthcare stakeholders want comprehensive functionality addressing every scenario. Feature lists grow continuously during development. But overloaded interfaces confuse users and slow workflows. Every additional feature increases cost, extends timelines, complicates testing, and multiplies potential failures.
Solutions
- Prioritize based on actual usage patterns and impact
- Build minimum viable products with core functionality
- Iterate based on real feedback, not assumptions
- Resist matching competitors feature-for-feature
- Focus on doing essential things exceptionally well
Challenge 6: Scalability planning
Problem
Initial deployments serve limited users and data volumes. But success brings growth (patient numbers increase, new locations open, data accumulates rapidly). Systems designed for current needs buckle under future loads. Retroactive scaling requires expensive reengineering, causes disruptions, and may necessitate complete rebuilds.
Solutions
- Design for scale from the beginning using cloud-based architectures
- Implement microservices architectures, scaling individual components independently
- Load test thoroughly with realistic data volumes
- Anticipate growth in the planning phase
- Budget for infrastructure costs increases with adoption
Recognizing these challenges early allows you to plan appropriate solutions rather than reacting to crises during development or after launch. Experienced providers offering custom healthcare software development solutions guide you through these obstacles using lessons learned across hundreds of projects.
Navigating these challenges successfully requires the right development partner with deep expertise in custom healthcare software development services.
Build Secure, Compliant Healthcare Software With Space-O Technologies
As healthcare continues to evolve, the need for secure, efficient, and patient-centric digital solutions has never been greater. From automating routine tasks to improving clinical decision-making and enhancing patient experiences, healthcare software plays a vital role in modernizing care delivery.
But developing healthcare software isn’t just about writing code. It requires deep industry understanding, careful attention to compliance, seamless interoperability with existing systems, and a user-first approach that supports both clinicians and patients. This is where working with an experienced healthcare software development partner makes all the difference.
At Space-O Technologies, we specialize in building custom healthcare software that is compliant, scalable, and tailored to your organization’s unique workflows. Our team has 15+ years of hands-on experience developing healthcare software solutions like EHR systems, telemedicine platforms, patient engagement apps, medical billing solutions, and AI-driven healthcare tools.
We follow a structured, transparent development process that ensures every product is secure, intuitive, and built to support long-term growth. If you’re ready to modernize your healthcare operations or bring a new digital solution to life, we’re here to help. Check our portfolio to see examples of our work and successful implementations in healthcare.
Conduet-Med: Mental Health Telehealth Platform
A cloud-based doctor-on-demand app enabling concierge patients to consult board-certified physicians remotely. Features include inquiry management, video consultations, secure messaging, and profile management for both doctors and patients. Designed for accessible healthcare delivery from thousands of miles away.
MedCall WorkComp: On-Demand Doctor Consultation App
A comprehensive telemedicine solution connecting patients with emergency physicians through video calls. Includes patient app, doctor app, and web portal for medical operators. Successfully serves 20,000 registered companies with over 200 active doctors providing tele-emergency triage and medical advice.
Pearson Dental Supply: Online Dental Equipment Store
An eCommerce platform offering 130,000 dental products with advanced barcode scanning, quick order functionality, and biometric authentication. Integrated with existing website infrastructure, enabling a seamless cross-platform shopping experience for dental professionals across categories, brands, and special offers.
Get in touch with us for a free consultation and discover how Space-O Technologies can turn your healthcare software vision into a reliable, future-ready solution.
Frequently Asked Questions About Healthcare Software Development
How long does healthcare software development take?
Timelines vary by complexity. Simple solutions like patient portals take 3–5 months, mid-level systems such as telemedicine platforms 6–9 months, and enterprise solutions with AI or multi-facility support 10–18 months. Agile development allows early deployment of core features, while experienced healthcare developers streamline workflows and reduce rework for faster delivery.
Can healthcare software integrate with existing EHR systems?
Yes. Modern healthcare software uses HL7, FHIR, and secure APIs for seamless integration with EHR, billing, lab, and imaging systems. This ensures unified access to patient data, eliminates duplicate entry, maintains consistency, and enables automated cross-system workflows. Integration planning begins during requirements analysis.
How do you ensure healthcare software is user-friendly for medical staff?
User adoption is key. Developers conduct user research, create personas, design intuitive workflows, prototype and test interfaces, follow accessibility standards, and provide responsive designs for all devices. Post-launch training, on-site support, and iterative updates based on feedback ensure smooth adoption.
What ongoing maintenance does healthcare software require?
Maintenance keeps software secure, compliant, and efficient. It includes security patches, compliance updates, performance optimization, bug fixes, feature improvements, infrastructure updates, and backup monitoring. Proper agreements cover SLAs, scheduled maintenance, 24/7 monitoring, and regular security assessments. Budget ~15–20% of the initial development cost annually.
How do you choose the right healthcare software development partner?
Choose a partner with domain expertise, proven compliance experience, a strong portfolio, and technical capabilities in custom healthcare software solutions. Ensure they follow agile methodologies, provide transparent communication, understand your workflows, and offer reliable post-launch support. Security certifications and client testimonials indicate credibility and quality.