Contents
A well-designed customer portal becomes a central platform for delivering consistent and efficient customer experiences.
Customer expectations have evolved significantly in recent years. Users now expect instant access to information, personalized experiences, and seamless digital interactions across every touchpoint. For businesses, meeting these expectations requires more than standalone applications or manual support processes.
Customer portal development focuses on building a secure, user friendly platform where customers can access services, manage accounts, track requests, and interact with your business independently. When implemented correctly, a customer portal improves engagement, reduces support workload, and creates long term value for both customers and internal teams.
In this blog, we explore everything you need to know to build a successful customer portal. Based on our 15+ years of experience as a trusted web portal development agency, we have shared insights on the fundamentals, benefits, essential features, development process, cost considerations, and best practices for building customer portals. Let’s get started.
What is Customer Portal Development?
Customer portal development is the process of designing and building a secure digital platform that allows customers to interact with a business through a centralized, self-service interface. A customer portal enables users to access information, manage their accounts, submit requests, track activities, and communicate with the business without relying on manual support channels.
Unlike generic customer-facing applications, custom customer portal development focuses on aligning the portal with specific customer journeys and internal business workflows. This includes defining user roles, permissions, and experiences that match how customers actually use the product or service. The goal is to create a consistent and intuitive experience while maintaining data security and system reliability.
A well-developed customer portal reduces support workload by enabling customers to resolve common tasks independently. It also improves engagement by offering real-time access to relevant data such as orders, subscriptions, tickets, invoices, or documents. For businesses, customer portals provide better visibility into customer interactions and help standardize service delivery.
Benefits of Developing a Customer Portal Platform
Building a custom customer portal delivers advantages that generic solutions cannot match. Organizations gain complete control over the user experience while addressing specific operational challenges. Here are the key benefits of building a customer portal platform:
1. Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
Customers today expect immediate access to information, regardless of business hours. A self-service portal provides 24/7 availability for account management, order tracking, and support requests. This convenience translates directly into higher customer satisfaction scores.
Personalized dashboards show each customer exactly what matters to them. Relevant information appears instantly without navigating through irrelevant content. Customers feel valued when the system recognizes their preferences and history.
2. Reduced support costs and ticket volume
High volumes of repetitive customer inquiries strain support teams and increase operational costs. A well-designed portal deflects common questions by providing self-service answers. Customers find information themselves instead of submitting support tickets. Knowledge bases, FAQ sections, and automated responses efficiently handle routine inquiries.
Support staff can then focus their expertise on complex issues that require human judgment. This allocation improves both efficiency and job satisfaction. Organizations typically see significant reductions in support ticket volume after deploying a portal. Lower ticket counts mean reduced staffing requirements or the ability to grow without proportional increases. The cost savings compound year over year.
3. Improved operational efficiency
Manual processes for document sharing, status updates, and client communication consume valuable staff time. A customer portal automates these workflows and eliminates redundant data entry. Information flows directly between systems without manual intervention. Staff no longer spend hours answering the same questions over and over throughout the day.
Automated notifications keep customers informed without requiring individual outreach. Freed-up capacity is redirected toward activities that generate revenue.
Standardized digital workflows ensure consistency across all customer interactions. Every client receives the same quality experience regardless of which staff member handles their account. Process compliance improves while training requirements decrease.
4. Increased customer retention and loyalty
Poor customer experience ranks among the top reasons clients leave for competitors. A professional portal demonstrates your commitment to client success and convenience. Customers who rely on your portal develop switching costs that promote retention.
Self-service capabilities let customers accomplish their goals on their own schedule and terms.
This empowerment builds positive associations with your brand. Satisfied customers renew subscriptions and expand their relationship with your business. Portal analytics reveal customer engagement patterns and potential churn indicators. Early intervention with at-risk customers becomes possible through data-driven insights. Proactive retention efforts yield higher lifetime customer value.
5. Competitive differentiation in the market
Many businesses still rely on email, phone calls, and outdated processes for customer interaction. Offering a modern portal positions your organization as innovative and customer-focused. This perception attracts prospects who value digital convenience.
Custom portal development enables unique features that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Proprietary workflows, specialized calculators, and industry-specific tools become sustainable advantages.
Your portal becomes a reason customers choose you over alternatives. White-label customer portal development allows agencies and service providers to offer branded experiences. Your clients see your brand throughout their digital interactions. This consistent branding strengthens professional perception.
6. Centralized customer data and insights
Customer interactions scattered across email, phone logs, and various systems create incomplete pictures. A portal centralizes all touchpoints into a unified customer record. Every interaction, document, and transaction lives in one accessible location. Centralized data enables meaningful analytics and reporting on customer behavior. Usage patterns reveal which features deliver the most value and which need improvement.
Data-driven decisions replace guesswork in product and service development.
Integration with CRM and business intelligence tools amplifies the value of portal data. Customer insights inform marketing campaigns, product roadmaps, and strategic planning. Your portal becomes a valuable business intelligence asset.
7. Scalability without proportional cost increases
Business growth traditionally requires proportional increases in support staff and infrastructure. A self-service portal handles growing customer bases without linear cost scaling. Technology investments deliver leverage that manual processes cannot match. Cloud-based portal architecture scales capacity automatically to meet demand spikes.
Peak periods no longer overwhelm staff or degrade customer experience. The system adapts to your growth rather than constraining it. Learn more about how to scale a web application to handle increasing user loads effectively.
Multi-location businesses benefit from centralized portal management with local customization options. New offices or regions gain immediate access to established self-service capabilities. Expansion becomes faster and more cost-effective.
Need a Custom-Developed Customer Portal for Your Business?
Space-O Technologies builds portals that align with your customer journeys and internal workflows.

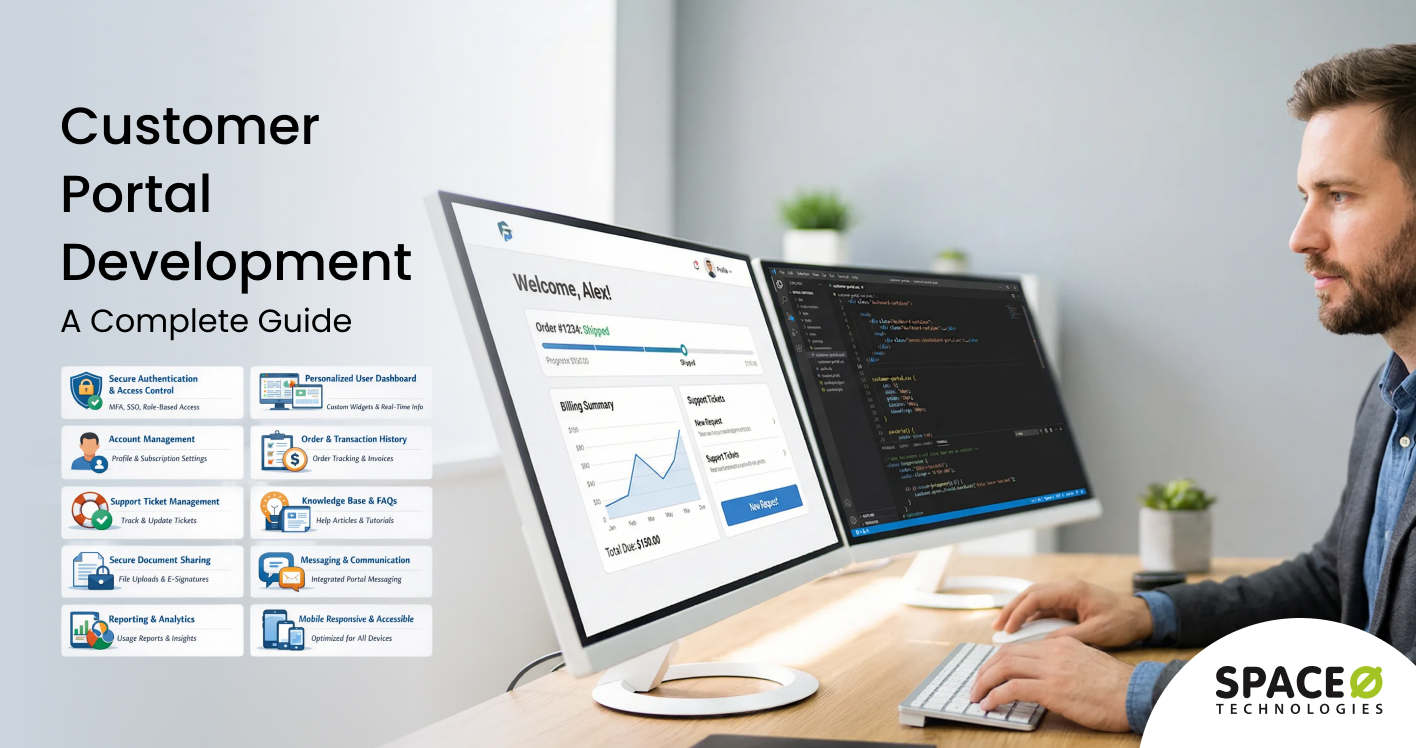
Core Features of a Customer Portal
Successful customer portals combine foundational capabilities with specialized features for specific industries. Understanding these components helps prioritize development investments. Let us explore the essential features that deliver value to both customers and businesses.
1. Secure user authentication and access control
Security is the foundation of any customer portal that handles sensitive information. Robust authentication ensures only authorized users access their accounts. Access control determines what each user can view and modify.
Essential capabilities include:
- Multi-factor authentication options for enhanced account security.
- Single sign-on integration with enterprise identity providers.
- Role-based access control for different user types.
- Password policies and secure recovery workflows.
- Session management with automatic timeout settings.
- Audit logging of all authentication events.
Strong security builds customer trust in your digital platform. Users feel confident sharing sensitive information when proper safeguards are in place. Security compliance also protects your organization from regulatory penalties.
2. Personalized user dashboard
The dashboard serves as the customer’s home base within your portal. It presents relevant information immediately upon login without requiring navigation. Effective dashboards anticipate what customers need most.
Essential capabilities include:
- Customizable widget layouts based on user preferences.
- Quick access to frequently used features and information.
- Real-time status updates for orders, tickets, and requests.
- Notification center for important alerts and messages.
- Recent activity history for quick reference.
- Account summary with key metrics at a glance.
Well-designed dashboards reduce time to complete common tasks. Customers find what they need without frustration or confusion. First impressions matter, and the dashboard shapes portal perception.
3. Account management and profile settings
Customers need control over their account information without contacting support. Self-service account management reduces administrative burden on your team. Empowered customers appreciate the ability to maintain their own records.
Essential capabilities include:
- Contact information updates with verification workflows.
- Communication preference management for notifications and marketing.
- Password and security settings modification.
- Subscription and plan management options.
- Payment method storage and updates.
- Account delegation to team members or family.
Self-service account management reduces inbound requests for basic changes. Customers make updates instantly rather than waiting for staff availability. Data accuracy improves when customers control their own information.
4. Order and transaction history
Customers frequently need to reference past orders, invoices, and transactions. Comprehensive history access eliminates inquiries that consume support resources. Detailed records also support customer decision-making for future purchases.
Essential capabilities include:
- Complete order history with filtering and search capabilities.
- Invoice and receipt viewing with download options.
- Order status tracking with shipment information.
- Reorder functionality for frequent purchases.
- Transaction details, including payment methods and dates.
- Export options for accounting and record-keeping purposes.
Access to transaction history answers many customer questions before they become tickets. Self-service research capabilities reduce wait times and improve satisfaction. Historical data also enables customers to identify spending patterns.
5. Support ticket management
Even with comprehensive self-service options, customers occasionally need human assistance. Integrated ticket management streamlines support interactions through the portal. Customers can track request status without having to repeatedly follow up.
Essential capabilities include:
- Ticket submission with categorization and priority options.
- File attachment support for screenshots and documentation.
- Ticket status tracking with update notifications.
- Conversation threading for ongoing support discussions.
- Satisfaction ratings after ticket resolution.
- Knowledge base suggestions before ticket creation.
Centralized ticket management improves support efficiency and customer experience. Agents see the complete context when responding to customer requests. Customers appreciate transparency into the support process.
6. Knowledge base and self-service resources
Comprehensive documentation empowers customers to solve problems independently. Knowledge bases reduce support volume by providing immediate answers. Well-organized resources become valuable additions to your customer experience.
Essential capabilities include:
- Searchable article library with categorization.
- Video tutorials and visual guides for complex processes.
- FAQ sections addressing common questions.
- Downloadable resources like manuals and templates.
- Community forums for peer-to-peer assistance.
- Feedback mechanisms to improve content quality.
Investing in knowledge content pays dividends by reducing support costs. Customers often prefer finding answers themselves over waiting for assistance. Quality self-service resources demonstrate your commitment to customer success.
7. Secure document sharing and storage
Many business relationships involve document exchange between organizations and customers. Secure portal storage eliminates insecure email attachments and scattered files. Centralized documents ensure customers always access current versions.
Essential capabilities include:
- Secure file upload and download functionality.
- Folder organization with intuitive navigation.
- Version control for documents with multiple iterations.
- E-signature integration for contracts and agreements.
- Access permissions control document visibility.
- Retention policies for compliance requirements.
Document management through the portal improves security and reduces administrative overhead. Customers access their files anytime without requesting staff assistance. Audit trails provide compliance documentation when required.
8. Communication and messaging
Direct communication channels within the portal keep conversations organized and accessible. Customers avoid searching email inboxes for past discussions. Integrated messaging also provides context for support interactions.
Essential capabilities include:
- Secure messaging with staff members and departments.
- Message threading for organized conversations.
- Read receipts and notification preferences.
- Automated message templates for common communications.
- Attachment support within conversations.
- Message search and archival capabilities.
Centralized communication improves response times and customer satisfaction. Staff see conversation history before responding to messages. Customers appreciate knowing their messages reach the right people.
9. Reporting and analytics
Customers benefit from insights into their own activity and usage patterns. Analytics dashboards help customers optimize their relationship with your business. Self-service reporting reduces requests for custom data exports.
Essential capabilities include:
- Usage analytics showing activity patterns over time.
- Spending summaries with trend visualization.
- Custom report generation with date range selection.
- Scheduled report delivery via email.
- Data export in common formats for external analysis.
- Comparative metrics against previous periods.
Customer-facing analytics add value beyond basic account management. Insights help customers make informed decisions about their engagement. Reporting capabilities differentiate your portal from simpler alternatives.
10. Mobile responsiveness and accessibility
Customers access portals from various devices, including smartphones and tablets. Mobile-responsive design ensures a consistent experience across screen sizes. Accessibility compliance opens your portal to customers with disabilities.
Essential capabilities include:
- Responsive layouts adapting to any screen size.
- Touch-friendly interface elements for mobile users.
- Offline capability for essential functions.
- Accessibility compliance with WCAG standards.
- Screen reader compatibility for visually impaired users.
- Keyboard navigation support.
Mobile accessibility expands when and where customers can engage with your portal. Failure to support mobile users excludes a significant portion of your audience. Accessibility compliance also protects against legal liability.
How to Build a Customer Portal Development: Complete Process
Building an effective customer portal follows a structured process that balances planning with iterative delivery. Understanding each phase helps set realistic expectations. Let us walk through the complete development journey.
Phase 1: Discovery and requirements analysis
Timeline: 3-6 weeks
Discovery establishes the foundation for your entire project. This phase documents customer needs, business objectives, and technical requirements. Rushing discovery creates expensive problems during later stages.
Key activities
- Stakeholder interviews: Conversations with customer success, support, sales, and IT teams reveal diverse perspectives. Each group contributes unique insights about customer pain points and desired capabilities.
- Customer research: Surveys, interviews, and usage data reveal what customers actually need from a portal. Understanding customer priorities ensures the portal delivers genuine value.
- Workflow documentation: Mapping current customer interaction processes exposes inefficiencies and automation opportunities. Visual process flows clarify handoffs and decision points.
- Technical assessment: Evaluating existing systems identifies integration requirements and the scope of data migration. Infrastructure capabilities determine deployment options.
- Competitive analysis: Reviewing how competitors serve customers through digital channels reveals opportunities for differentiation. Industry best practices inform feature priorities.
- Prioritization workshops: Stakeholders rank features by customer value and business impact. This prioritization drives development sequencing.
Discovery delivers requirements documentation, technical architecture recommendations, and a prioritized feature roadmap. Thorough discovery prevents costly mid-project pivots.
Phase 2: System design and architecture
Timeline: 2-4 weeks
Design translates requirements into technical specifications and visual prototypes. This phase defines how the portal will function and appear. Stakeholder approval of designs prevents expensive development changes.
Key activities
- Architecture design: Technical architects define database structure, application layers, and infrastructure requirements. Scalability and security considerations shape foundational decisions.
- User interface design: UX designers create wireframes and interactive prototypes visualizing portal behavior. Customer testing validates designs before development begins.
- Integration planning: Detailed specifications define how the portal connects with CRM, ERP, and other business systems. API designs establish data exchange protocols.
- Security design: Authentication mechanisms, encryption standards, and access control models are explicitly defined. Compliance requirements drive security architecture.
- Mobile strategy: Decisions about responsive web design versus native mobile apps align with customer usage patterns. Technical specifications address mobile-specific requirements.
Design deliverables include technical specifications, interface mockups, and integration documentation. Approval gates ensure alignment before development investment.
Phase 3: Development and implementation
Timeline: 8-24 weeks, depending on scope
Development transforms designs into working software through iterative delivery cycles. The web development process follows agile methodologies that enable early feedback and course correction. Regular demonstrations keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
Key activities
- Sprint-based development: Two-week sprints deliver testable functionality at regular intervals. Product owners review progress and adjust priorities based on emerging needs.
- Frontend development: User interface components bring designs to life with responsive, accessible implementations. Performance optimization ensures fast load times.
- Backend development: Server-side logic implements business rules, manages data, and establishes integration connections. API development enables system interoperability.
- Integration implementation: Connections to existing business systems bring customer data into the portal. Data transformation ensures compatibility between systems.
- Continuous integration: Automated testing validates code quality with every change. Issues surface immediately rather than accumulating for later discovery.
Development follows the prioritized roadmap while maintaining flexibility for scope adjustments. Regular stakeholder demonstrations maintain alignment throughout the process.
Phase 4: Testing and quality assurance
Timeline: 3-6 weeks (overlapping with development)
Comprehensive testing ensures the portal meets requirements while maintaining performance standards. Quality assurance protects your investment and customer relationships.
Key activities
- Functional testing: Test cases verify every feature works as specified. Edge cases and error conditions receive explicit attention.
- Integration testing: End-to-end workflows validate behavior across connected systems. Data flows correctly between the portal and business applications.
- Performance testing: Load testing confirms portal capacity under expected and peak usage patterns. Performance bottlenecks receive attention before launch.
- Security testing: Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning identify security weaknesses. Compliance audits verify regulatory adherence.
- User acceptance testing: Real customers validate portal behavior in realistic scenarios. Feedback drives final refinements before launch.
- Accessibility testing: Verification against WCAG standards ensures the portal works for all users. Assistive technology compatibility receives explicit testing.
Quality assurance should not be compressed to meet deadlines. Undiscovered defects damage customer trust and require expensive remediation.
Phase 5: Deployment and launch
Timeline: 2-4 weeks
Deployment transitions the portal from development to production use. Careful planning minimizes disruption while ensuring successful adoption.
Key activities
- Data migration: Historical customer data transfers from existing systems into the portal. Validation confirms accuracy and completeness.
- User onboarding preparation: Welcome emails, user guides, and tutorial content prepare customers for the new portal. Clear instructions reduce confusion.
- Training delivery: Internal teams receive training on portal administration and customer support procedures. Staff confidence enables effective customer assistance.
- Soft launch: Limited release to a customer subset validates production behavior. Issues surface and receive resolution before broad availability.
- Full launch: Public availability with communication campaigns drives customer adoption. Support resources handle initial questions effectively.
Phased rollouts reduce risk for significant customer portal deployments. Starting with willing early adopters validates processes before broader release.
Phase 6: Ongoing support and enhancement
Timeline: Continuous
Post-launch support ensures system stability while enabling continuous improvement. Customer portals require ongoing attention to maintain value.
Key activities
- Bug fixes and patches: Issues discovered in production receive prompt resolution. Severity-based prioritization ensures critical problems get immediate attention.
- Performance monitoring: System health metrics identify capacity needs and performance degradation. Proactive intervention prevents customer-facing issues.
- Customer feedback analysis: Usage data and feedback reveal opportunities for improvement. Customer input drives enhancement priorities.
- Feature enhancements: New capabilities respond to evolving customer needs and business requirements. The portal improves continuously.
- Security updates: Regular patching addresses emerging vulnerabilities. Security monitoring detects and responds to threats.
Budget for ongoing support from project inception. Portals without maintenance degrade over time and eventually require replacement.
Let Our Expert Portal Developers Handle the Process
Space-O Technologies has helped 1200+ clients build custom digital platforms. Let’s discuss your customer portal requirements.
Customer Portal Development Cost Breakdown
Understanding cost components helps organizations budget accurately for portal development. Costs vary based on complexity, features, and development approach. For additional context on digital platform investments, review our guide on web app development cost. Let us examine the factors that influence investment requirements.
Cost by implementation scope
| Scope Level | Development Cost Range | Timeline | Features Included |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Portal | $30,000 – $75,000 | 2-4 months | Login, dashboard, account management, basic support |
| Standard Portal | $75,000 – $175,000 | 4-7 months | Basic features + document management, knowledge base, integrations |
| Advanced Portal | $175,000 – $350,000 | 6-10 months | Standard features + advanced analytics, automation, mobile apps |
| Enterprise Portal | $350,000 – $750,000+ | 10-16 months | Advanced features + multi-tenant, white-label, complex integrations |
Cost breakdown by development phase
| Phase | Budget Allocation | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery and Requirements | 8-12% | Stakeholder interviews, customer research, workflow documentation |
| Design and Architecture | 10-15% | UI/UX design, technical architecture, integration planning |
| Development | 45-55% | Frontend, backend, integration implementation |
| Quality Assurance | 15-20% | Functional, integration, performance, and security testing |
| Deployment and Training | 8-12% | Data migration, user onboarding, launch support |
| Project Management | 10-15% | Coordination, communication, risk management |
Factors that influence development costs
Several variables push costs toward higher ranges. Understanding these factors helps set realistic budgets.
- Integration complexity: Each external system integration adds $8,000 to $40,000, depending on the availability of the API. Legacy systems without modern APIs require custom middleware development.
- Security and compliance requirements: Enterprise security standards add 10-20% to baseline costs. Industry-specific compliance, like HIPAA or SOC 2, increases scope and testing requirements.
- Custom reporting and analytics: Advanced dashboards with custom metrics and data visualization significantly expand the development scope. Real-time analytics require additional infrastructure investment.
- Mobile applications: Native iOS and Android apps double or triple the user interface development effort. Cross-platform frameworks reduce but do not eliminate this multiplier.
- Multi-language support: Internationalization adds complexity to content management and user interface development. Each supported language requires translation and testing effort.
- White-label capabilities: Building for rebranding and resale adds architectural complexity. Multi-tenant requirements increase the scope of development and testing.
Hybrid models combining onshore project management with offshore development optimize both quality and cost. This approach delivers substantial savings compared to fully domestic development while maintaining communication effectiveness.
Ongoing cost considerations
Initial development represents only part of the total ownership cost. Plan for ongoing expenses.
- Annual maintenance: 15-20% of the initial development cost covers bug fixes, security patches, and minor enhancements.
- Infrastructure: Cloud hosting costs range from $300 to $3,000 per month, depending on user volume and data storage requirements.
- Security maintenance: Annual security audits and penetration testing cost $8,000 to $25,000.
- Feature enhancements: Budget $40,000 to $120,000 annually for new functionality responding to customer feedback and business needs.
Get an Accurate Customer Portal Development Estimate
Share your requirements with our technical team for a detailed cost breakdown tailored to your specific needs.
Common Challenges in Customer Portal Development
Even well-planned projects encounter obstacles along the way. Anticipating challenges enables proactive mitigation rather than reactive crisis management. Let us examine common issues and solutions.
Challenge 1: Low customer adoption after launch
Building a portal does not guarantee customers will use it. Habits form around existing communication channels like phone and email. Poor adoption undermines return on investment.
How to overcome this challenge
- Design intuitive interfaces that require minimal learning for basic tasks.
- Communicate clear value propositions that motivate customers to try the portal.
- Provide multiple onboarding touchpoints, including emails, tutorials, and in-app guidance.
- Incentivize initial use with exclusive content or features available only on the portal.
- Measure adoption metrics and address barriers identified through customer feedback.
Challenge 2: Integration complexity with existing systems
Customer portals must integrate with CRM, ERP, billing systems, and other business systems. Legacy applications often lack modern APIs or have incomplete documentation. Data inconsistencies between systems create additional complications.
How to overcome this challenge
- Conduct a thorough technical assessment of all integration targets during discovery.
- Budget additional time for systems with poor documentation or outdated APIs.
- Build data validation and transformation layers to handle inconsistencies.
- Plan parallel operation periods before decommissioning manual processes.
- Document integration specifications comprehensively for future maintenance.
Challenge 3: Balancing security with user convenience
Strong security measures can create friction that frustrates customers. Password complexity, multi-factor authentication, and session timeouts interrupt the user experience. Finding the right balance requires careful consideration.
How to overcome this challenge
- Implement risk-based authentication that adjusts requirements based on context.
- Offer multiple authentication options so customers can choose their preferred method.
- Use remembered device features to reduce friction for trusted equipment.
- Provide a clear explanation of security measures so customers understand their protection.
- Test security workflows with real customers to identify unnecessary friction.
Challenge 4: Scope creep during development
Requirements evolve as stakeholders interact with developing software. Feature requests accumulate and expand scope beyond initial estimates. Uncontrolled growth delays delivery and inflates costs.
How to overcome this challenge
- Establish formal change request processes that assess impact before approval.
- Build contingency budgets of 15-20% for approved scope additions.
- Use phased delivery to defer non-essential features to subsequent releases.
- Maintain clear prioritization criteria tied to customer and business value.
- Document decisions thoroughly to prevent regression of requirements.
Challenge 5: Maintaining consistent experience across devices
Customers access portals from desktops, tablets, and smartphones with different screen sizes. Ensuring consistent functionality and appearance across devices creates design and development challenges. Mobile-specific requirements add complexity.
How to overcome this challenge
- Adopt mobile-first design approaches that scale up to larger screens.
- Test extensively on multiple device types and screen sizes throughout development.
- Prioritize essential mobile functionality while providing enhanced desktop experiences.
- Use responsive frameworks that handle common device adaptation automatically.
- Monitor device analytics post-launch to focus optimization efforts.
Challenge 6: Data migration from legacy systems
Moving historical customer data into the new portal creates unexpected challenges. Data quality issues, format inconsistencies, and volume limitations complicate migration. Errors during migration damage customer trust.
How to overcome this challenge
- Assess data quality early to identify cleanup requirements.
- Develop data transformation rules with business stakeholder input.
- Plan multiple migration test cycles before production cutover.
- Establish data validation checkpoints throughout the migration process.
- Maintain rollback capabilities until migration verification completes.
Addressing these challenges early transforms customer portal development from a risky initiative into a predictable, value-driven investment. With thoughtful planning, user-centric design, and strong technical execution, organizations can deliver portals that drive adoption, trust, and long-term customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Successful Customer Portal Development
Following proven practices dramatically increases project success rates. These guidelines represent accumulated wisdom from successful implementations. Let us explore how to maximize your portal investment.
1. Start with customer research
Understanding actual customer needs prevents the creation of features nobody uses. Assumptions about what customers want often prove incorrect. Direct research reveals real priorities. Our guide to creating a web application covers the research and planning phases in detail.
Survey existing customers about their pain points and desired self-service capabilities. Interview representative customers from different segments for deeper insights. Analyze support ticket data to identify common questions the portal could answer.
Let customer input drive feature prioritization rather than internal assumptions. Validate designs with customer feedback before committing to development. Continue gathering feedback throughout development and after launch.
2. Prioritize user experience above features
Portals succeed or fail based on whether customers actually use them. Complex interfaces with many features often perform worse than simple, focused designs. Ease of use matters more than feature count.
Design for the most common tasks customers need to accomplish. Minimize clicks and steps required to complete frequent activities. Test designs with real customers before development begins.
Consider the complete user journey from login through task completion. Remove friction at every point in the experience. Simple, intuitive workflows encourage adoption and build positive associations.
3. Plan integrations carefully from the start
Integration complexity often exceeds initial estimates. Each connected system brings unique data models and technical requirements. Underestimating integration work creates project delays.
Map all integration points during discovery. Assess API availability, documentation quality, and vendor support responsiveness. Budget additional time for systems with poor documentation.
Build integration monitoring and error handling from day one. Connections fail occasionally. Graceful handling and quick notification minimize downstream customer impact.
4. Build security into the foundation
Security must shape architecture decisions from project inception. Adding security to completed systems creates vulnerabilities and rework. Foundational security protects both customers and your organization.
Engage security expertise early in the project. Industry-specific requirements, such as HIPAA or financial regulations, require specialized knowledge. Security architects should review designs before development begins.
Document security measures comprehensively. Auditors require evidence of controls. Well-documented systems pass security reviews faster with less disruption.
5. Implement iterative delivery
Delivering functionality incrementally provides multiple benefits. Stakeholders see progress and provide feedback early. Course corrections happen before significant investment accumulates.
Two-week development sprints work well for most portal projects. Longer iterations delay feedback while shorter ones create overhead. Regular demonstrations maintain stakeholder alignment.
Prioritize delivery of core workflows first. Customers can begin benefiting from basic portal features while advanced capabilities are developed. Early value delivery builds organizational support.
6. Invest in customer onboarding
Portal launch marks the beginning, not the end, of the adoption journey. Customers need guidance to discover and use portal capabilities effectively. Poor onboarding undermines development investment.
Create multiple onboarding touchpoints, including welcome emails, guided tours, and video tutorials. Address diverse learning preferences with a range of content formats. Make help accessible within the portal interface.
Track onboarding completion and identify where customers struggle or abandon. Iterate on onboarding content based on customer behavior data. Successful onboarding leads to long-term engagement.
7. Plan for continuous improvement
Customer portals are never truly complete. Customer needs evolve, technology changes, and competitors improve. Static portals eventually become liabilities.
Build systems that accommodate change through modular architecture and clean code practices. Comprehensive documentation enables efficient future modification. Plan for capacity enhancement from project inception.
Establish continuous feedback loops to capture customer input. Usage analytics reveal which
features deliver value and which need improvement. Let data drive enhancement priorities.
Build a Custom Customer Portal with Space-O Technologies
Customer portal development transforms how organizations engage with their clients. Custom solutions eliminate compromises that off-the-shelf software requires. Your portal works exactly as your customers need it to.
Success requires more than technical capability alone. Understanding customer expectations, industry requirements, and adoption challenges determines whether projects deliver lasting value. Experience with similar implementations accelerates delivery and reduces risk.
Space-O Technologies brings extensive expertise in custom software development to customer portal projects. Our team has delivered numerous software solutions, including customer-facing platforms serving diverse industries. We hold ISO 27001:2022 certification for information security and ISO 9001:2022 for quality management. Our teams understand the security and compliance requirements that customer portals demand.
Contact us to discuss your customer portal requirements. We provide detailed assessments, realistic cost estimates, and development roadmaps tailored to your specific situation.
FAQs on Customer Portal Development
1. How much does customer portal development cost?
Customer portal development costs range from $30,000 for basic systems to $750,000+ for enterprise-grade platforms. Basic portals with login, dashboard, and account management cost $30,000 to $75,000. Standard systems with document management and integrations cost $75,000 to $175,000. Advanced platforms with analytics and mobile apps cost $175,000 to $350,000. Enterprise portals with white-label and complex integrations exceed $350,000.
2. How long does it take to build a customer portal?
Development timelines vary from 2-4 months for basic portals to 10-16 months for enterprise implementations. Basic projects with core features typically take 2-4 months to complete. Standard implementations requiring integrations take 4-7 months. Advanced projects with extensive features require 6-10 months. Enterprise deployments with complex requirements take 10-16 months, including phased rollouts.
3. What features are essential in a customer portal?
Essential customer portal features include secure authentication, personalized dashboard, account management, order and transaction history, support ticket management, knowledge base, document sharing, messaging, and mobile responsiveness. The specific feature set depends on industry requirements and customer needs. Additional capabilities like analytics, automation, and integrations add value for more complex use cases.
4. Should I build a custom customer portal or use an existing platform?
The decision depends on several factors. Custom development suits organizations with unique workflows that existing platforms cannot accommodate. It also benefits companies seeking competitive differentiation through proprietary capabilities. Organizations with large customer bases benefit from eliminating per-user licensing fees. Existing platforms work better for smaller companies with standard requirements, limited budgets, and immediate implementation needs.
5. How do you ensure the security of the customer portal?
Customer portal security requires architectural decisions from project inception. Key measures include encryption for data at rest and in transit. Role-based access controls limit data visibility. Multi-factor authentication options protect accounts. Comprehensive audit logging tracks all data access. Regular security assessments identify vulnerabilities. Penetration testing validates security measures. Development teams need security expertise to implement these measures correctly.
6. Can a customer portal integrate with existing business systems?
Yes, modern customer portals integrate with CRM, ERP, billing, and other business systems using APIs. Integration typically includes customer data synchronization, order and transaction exchange, and support ticket coordination. Integration complexity depends on the specific systems involved. Platforms with well-documented APIs integrate more easily than legacy systems without modern integration capabilities.