Every powerful digital product, from mobile apps to enterprise platforms, relies on one thing in common: a well-built backend. It’s the unseen engine that processes data, connects systems, and ensures everything users see on the frontend works flawlessly.
In today’s digital landscape, backend development isn’t just about managing servers or databases. It’s about designing intelligent, scalable systems that power seamless experiences and business growth.
Whether you’re launching a startup application or modernizing a legacy system, your backend determines how well your product performs, scales, and adapts to change.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about backend development, including the core components, architectures, technologies, and development process. Understand why strong backends are essential for building reliable, future-ready applications and how you can find a reliable backend development company to build your solution.
Table of Contents
What Is Backend Development?
Backend development refers to the server-side of web, mobile, or software applications, the part that users don’t see but that makes everything work smoothly behind the scenes. It’s responsible for handling data, processing business logic, and ensuring that user requests from the frontend (the visible interface) are executed correctly and efficiently.
In simple terms, the backend is the brain of an application. When you log in, make a payment, or request information from a website, it’s the backend that communicates with the database, applies rules, and sends the right response back to the frontend.
A typical backend includes three key layers:
Server: The environment that hosts and runs the application
Database: Where data is stored, organized, and retrieved
Application: The logic that processes requests and controls how data is used
Together, these components ensure that every user action, from form submissions to search queries, happens securely, accurately, and instantly.
Backend development also plays a crucial role in scalability, security, and performance. Businesses hire back-end developers to build a well-structured backend that allows apps to handle more users, integrate with external systems, and deliver fast, seamless experiences, no matter how complex the application grows.
In short, backend development is what turns a static interface into a functional, data-driven digital experience that users can rely on every day. Next, let’s understand the components that make up a system’s backend.
Key Components of Backend Development
Backend development is built on a foundation of core components that work together to power an application’s logic, functionality, and performance. These components ensure that every user interaction is processed accurately, data is managed efficiently, and the application runs smoothly at scale.
Let’s break down the main elements that make up the backend.
Servers
A server is the backbone of any backend system. It’s a powerful computer or cloud environment that hosts applications, stores data, and processes user requests coming from the frontend.
When a user interacts with a website or app, for example, by logging in or viewing a profile, the server receives that request, processes it according to predefined rules, and sends back the appropriate response, such as account details or confirmation messages.
Modern backend systems often use cloud servers (like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure) for better scalability, uptime, and performance. These allow applications to handle thousands of simultaneous requests seamlessly and ensure high availability for global users.
Databases
A database is where all application data lives, from user information and transactions to content and configurations. Backend development relies on databases to store, organize, retrieve, and manage data efficiently.
- Relational Databases (SQL): These use structured tables with rows and columns, making them ideal for applications that require complex queries and strong data consistency. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL): These store data in flexible formats like key-value pairs or documents. They’re great for unstructured or rapidly changing data. Popular examples include MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis.
There are two main types of databases:
Choosing the right database impacts scalability, performance, and reliability. For instance, eCommerce apps may prefer relational databases for order tracking, while social media platforms might use NoSQL for handling large, dynamic user data.
APIs and middleware
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the bridges between the frontend and backend. They define how different software components interact. They allow the frontend to send requests and the backend to deliver responses in a structured format, usually JSON or XML.
- REST (Representational State Transfer): The most widely used API architecture, known for simplicity and flexibility
- GraphQL: A modern alternative that lets clients request exactly the data they need, improving efficiency and reducing over-fetching
The two most common types of APIs are:
Middleware acts as a layer between the server and application logic. It performs essential functions such as data validation, authentication, logging, and error handling, ensuring secure and efficient communication between system components.
Together, APIs and middleware form the communication backbone of backend development — connecting users, applications, and services seamlessly.
Server-side languages
Server-side programming languages power the logic that makes applications function. These languages handle everything from processing data to managing user authentication and connecting to databases.
- Python: Widely used for web development, AI, and data-driven applications (frameworks like Django and Flask)
- Java: Ideal for large-scale enterprise systems and Android apps due to its stability and scalability
- PHP: Commonly used for CMS platforms like WordPress and eCommerce websites (frameworks like Laravel)
- Node.js (JavaScript): Great for real-time applications such as chat apps or streaming services
- Go (Golang): Known for its speed and efficiency, often used for cloud-based and microservices architectures
- Ruby: Popular for rapid web development using the Ruby on Rails framework
Here are some of the most popular backend languages and their typical use cases:
The choice of language depends on project needs, whether it’s speed, scalability, or ecosystem maturity.
Each of these backend components plays a vital role in ensuring that digital products are fast, secure, and reliable. Next, let’s understand the different types of backend architecture and how they impact the backend’s performance.
Turn Your Backend Vision Into a Reliable Backend System
A strong architecture starts with the right backend strategy. At Space-O Technologies, we build secure, high-performance backend systems that scale with your business.
Backend Development Architecture
The architecture of a backend system defines how its components are structured, connected, and scaled. Choosing the right architecture directly affects an application’s performance, scalability, and maintenance.
There are several architectural patterns used in backend development. Each is suited for different project sizes and goals. Let’s explore the three most common ones.
Monolithic architecture
In a monolithic architecture, the entire application, including the frontend, backend logic, and database, is built as a single, unified unit. All features and functions are tightly connected and run within the same codebase and server environment.
Structure of monolithic architecture
- A single code repository for all modules
- Shared database and resources
- One deployment unit, updates or changes affect the entire system
Advantages of monolithic architecture
- Simplicity: Easier to develop, test, and deploy for small teams
- Performance: Faster internal communication since all components are integrated
- Cost-effective: Ideal for small projects or startups with limited resources
When to use monolithic architecture
- Early-stage products or MVPs
- Applications with well-defined, limited functionality
- Teams that prioritize speed of development over scalability
While monolithic systems are easy to start with, they can become difficult to maintain or scale as the application grows. This makes it harder to introduce new features or technologies independently.
Microservices architecture
Microservices architecture breaks down an application into smaller, independent services, each handling a specific business function, such as user authentication, payments, or notifications. These services communicate with each other via APIs.
Structure of microservices architecture
- Each service has its own codebase, database, and deployment pipeline
- Communication between services via REST APIs, gRPC, or event streams
- Independent scaling and versioning for each service
Advantages of microservices architecture
- Scalability: Individual services can scale independently based on demand
- Faster development and deployment: Teams can work on separate services simultaneously
- Resilience: Failure in one service doesn’t take down the entire system
- Flexibility: Different services can use different languages or frameworks
When to use microservices architecture
- Large-scale or rapidly growing applications
- Projects requiring high uptime and flexibility
- Teams practicing continuous delivery and DevOps
Microservices are ideal for organizations aiming for agility, scalability, and innovation, though they require strong infrastructure and coordination to manage multiple services effectively.
Serverless and cloud-based backends
Serverless architecture represents the next evolution in backend development. In this model, developers focus purely on writing code while cloud providers handle server management, scaling, and infrastructure.
Applications are built around functions that automatically run in response to specific events (like user actions or database updates). You only pay for what you use, making this model cost-efficient and scalable.
Structure of serverless and cloud-based backends
- Application logic is split into functions triggered by events (like API calls, file uploads, or user actions)
- No fixed servers; cloud providers manage compute resources dynamically
- Integrated with cloud-based databases, storage, and APIs
Advantages of serverless and cloud-based backends
- No server management: The cloud provider (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) handles provisioning and scaling
- Cost efficiency: You pay only for execution time, not idle resources
- Automatic scaling: Functions scale up or down instantly based on traffic
When to use serverless and cloud-based backends
- Applications with variable workloads or unpredictable traffic
- Projects that need rapid deployment without infrastructure setup
- Lightweight, event-driven use cases like chatbots, APIs, and IoT systems
Serverless and cloud-based architectures empower businesses to build scalable, resilient applications faster, reducing operational overhead while ensuring high availability.
Each architecture, monolithic, microservices, or serverless, serves a unique purpose. The right choice depends on your project’s size, performance needs, and long-term growth strategy. Next, let’s explore the key backend development technologies and frameworks.
Backend Development Technology Stack: Languages, Frameworks, and Tools You Need to Know
Ever wondered what makes an app fast, reliable, and scalable? It all comes down to the technology stack running behind the scenes. From programming languages to frameworks and cloud tools, each layer plays a vital role in shaping performance and user experience.
Backend development programming languages
- Python: Excels in data-heavy applications and MVPs with an easy learning curve and moderate performance. Widely used in AI, machine learning, and data analytics for its vast ecosystem and flexibility.
- JavaScript: Handles real-time applications and APIs with good performance and easy learning. Its versatility across frontend and backend makes it ideal for full-stack development.
- Java: Dominates enterprise systems with excellent performance despite a moderate learning curve. Renowned for its scalability, security, and compatibility across large-scale applications.
- PHP: Powers web applications and CMS platforms with good performance and easy adoption. Laravel and Symfony frameworks make PHP particularly strong for content-driven websites.
- Ruby: Accelerates startup development with rapid prototyping capabilities and moderate performance. Ruby on Rails remains popular for MVPs and SaaS products.
- Go: Delivers high performance for microservices and cloud applications with a moderate learning curve. Its concurrency model and speed make it excellent for distributed systems.
Backend development frameworks
- Express.js: Provides a minimalist, flexible framework for building web applications and APIs quickly. Its unopinionated structure lets developers choose tools matching project needs.
- Django: Offers a batteries-included framework with built-in admin panels, authentication, and ORM. It accelerates development for content management systems, social platforms, and data-driven applications.
- Spring Boot: Simplifies enterprise application development with robust dependency injection, security features, and microservices support, commonly used in banking, insurance, and government systems.
- Laravel: Delivers elegant syntax and powerful features, including routing, authentication, and task scheduling. Its ecosystem supports rapid development of modern web applications with clean, maintainable code.
- Ruby on Rails: Follows convention-over-configuration principles, enabling rapid MVP development. Its mature ecosystem and built-in features make it ideal for startups validating business ideas quickly.
- NestJS: Brings TypeScript support and Angular-like architecture to backend development. Its modular structure suits complex enterprise applications requiring maintainability and scalability.
Pro Tip: When selecting backend frameworks, consider your project’s scalability, security needs, and long-term maintenance. The right choice can simplify development and accelerate product success.
Database management systems
- Relational databases (SQL) (PostgreSQL and MySQL): Organize data in structured tables with defined relationships. They enforce data integrity through ACID properties, making them reliable for financial systems, e-commerce platforms, and applications requiring complex queries.
- NoSQL databases (MongoDB and Cassandra): offer flexible schemas and horizontal scalability. They excel in handling large volumes of unstructured data, real-time analytics, and applications requiring rapid development iterations.
- In-memory databases (Redis and Memcached) Store data in RAM for extremely fast access. They power caching layers, session management, and real-time features, reducing database load by 70% or more.
Now that we’ve explored the core technologies powering backend development, let’s understand why a strong backend is critical to business success.
Leverage the Right Tech Stack With Space-O Technologies
Our team specializes in Node.js, Python, Java, Go, PHP, and cloud-native technologies to build backends that are fast, secure, and future-ready.
Why Backend Development Matters for Businesses
The backend is much more than just code running behind the scenes; it’s the foundation that keeps your application secure, scalable, and efficient. Whether you’re building a mobile app, a SaaS platform, or an enterprise system, the quality of your backend directly impacts user satisfaction and business performance.
Ensures Scalability and Performance
As your business grows, so does the number of users, requests, and integrations your system must manage. A strong backend allows your application to handle high traffic volumes, complex transactions, and data-intensive processes without crashing or slowing down.
A well-architected backend ensures that performance remains stable even under heavy load by using tools like load balancers, caching, and distributed databases. In essence, it enables your digital platform to scale seamlessly, supporting growth without compromising speed or reliability.
Protects Data and Enhances Security
Security is a top priority for every digital business, and backend development plays a central role in safeguarding sensitive information. Modern backends are built with advanced security protocols that handle:
- User authentication and authorization
- Data encryption during storage and transmission
- Access control and activity logging to prevent breaches
A secure backend helps protect both your customers’ privacy and your company’s reputation. By implementing security best practices at the backend level, businesses can prevent data leaks, fraud, and unauthorized access, ensuring trust and compliance with global regulations.
Powers Automation and Integrations
Backend systems act as the bridge between your application and external tools, enabling seamless automation and data flow. Through APIs and middleware, your backend can connect with:
- CRM and ERP platforms for unified business management
- Payment gateways and third-party services for smooth transactions
- Analytics tools and AI systems for smarter decision-making
These integrations eliminate manual work, reduce errors, and create automated, efficient workflows that enhance productivity and operational visibility.
Enables Personalized User Experiences
In today’s digital landscape, personalization is key to engagement and retention, and the backend makes it possible. By storing and analyzing user data such as preferences, purchase history, and behavior patterns, the backend dynamically delivers customized content, recommendations, and interactions.
For example, streaming platforms suggest shows based on past views, and eCommerce sites display products aligned with browsing history, all powered by backend intelligence. This data-driven personalization leads to better customer satisfaction, stronger brand loyalty, and higher conversion rates.
A well-built backend is not just a technical necessity. It’s a strategic asset that supports scalability, enhances security, drives automation, and delivers personalized experiences that keep users coming back. Next, let’s understand how backends are developed.
Transform Your Business with a Stronger Backend
At Space-O Technologies, we help businesses build secure, scalable, and future-ready backend systems that enhance performance, support growth, and unlock innovation.
The Backend Development Process: From Planning to Deployment
Building a reliable backend requires a structured process that transforms ideas into fully functional, secure, and scalable systems. Each stage, from planning to deployment, plays a critical role in ensuring performance, reliability, and maintainability.
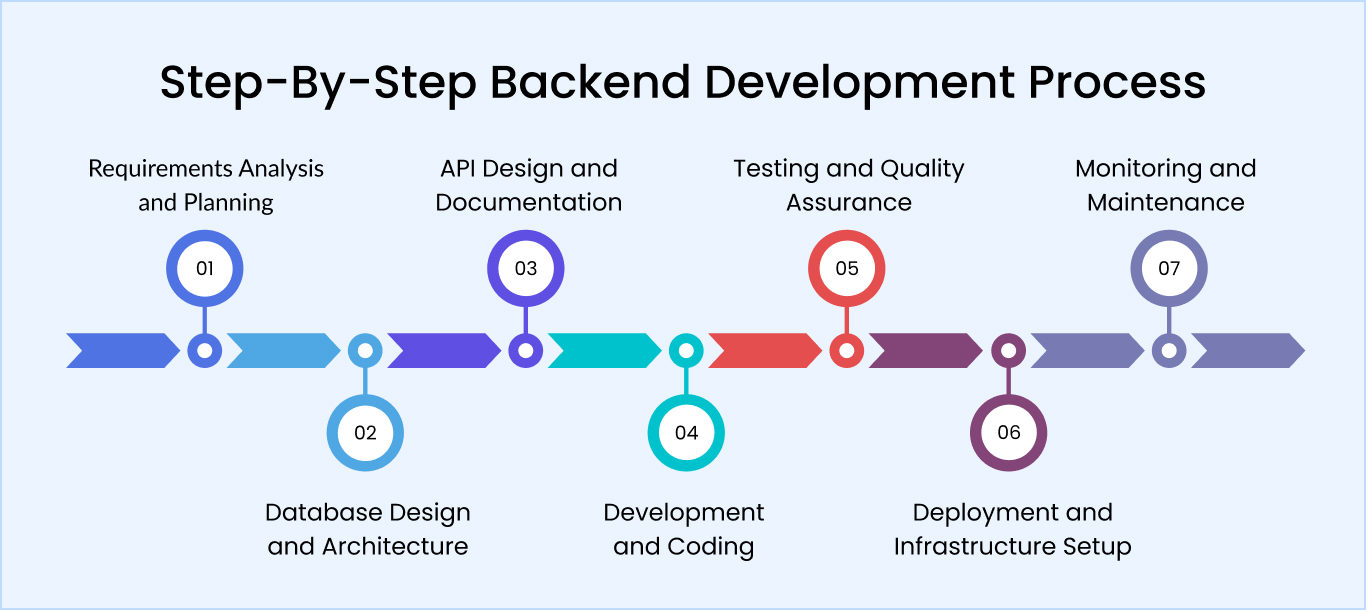
Backend planning
.
Backend development starts with understanding business needs and technical requirements. Developers define features, traffic expectations, security needs, and integrations. They select the technology stack, create specifications, and establish milestones for delivery.Database design and architecture
Developers design database schemas, organizing data logically while minimizing redundancy. They choose between SQL and NoSQL based on requirements, create indexes for performance, and implement backup procedures protecting against data loss.
API design and documentation
APIs define how applications interact with backend systems. Developers design RESTful or GraphQL endpoints following standards, version APIs for compatibility, and create comprehensive documentation explaining authentication, available endpoints, and error handling.
Development and coding
Developers write server-side logic processing requests, validating inputs, and executing business rules. They follow coding standards, write clean, maintainable code, and conduct code reviews, ensuring quality and catching issues early.
Testing and quality assurance
Testing verifies that systems work correctly under various conditions. Developers write unit, integration, and end-to-end tests. Automated testing catches regressions, load testing ensures traffic handling, and security testing identifies vulnerabilities.
Deployment and infrastructure setup
Deployment transfers code to production servers. Developers configure infrastructure using containerization platforms like Docker and Kubernetes. CI/CD pipelines automate deployment, running tests, and promoting code to production with minimal downtime.
Monitoring and maintenance
Post-deployment monitoring tracks application health and identifies issues early. Developers implement logging, set up alerts, and visualize metrics through dashboards. Regular maintenance includes security patches, dependency updates, and performance optimization.
Even with the best planning and execution, backend development comes with its share of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions helps you build more resilient systems.
Common Backend Development Challenges and How to Solve Them
Whether you need mobile app backend development or a web platform, most projects face similar challenges around scalability, security, performance, and code quality. Addressing these backend issues ensures your app stays robust and responsive as it grows.
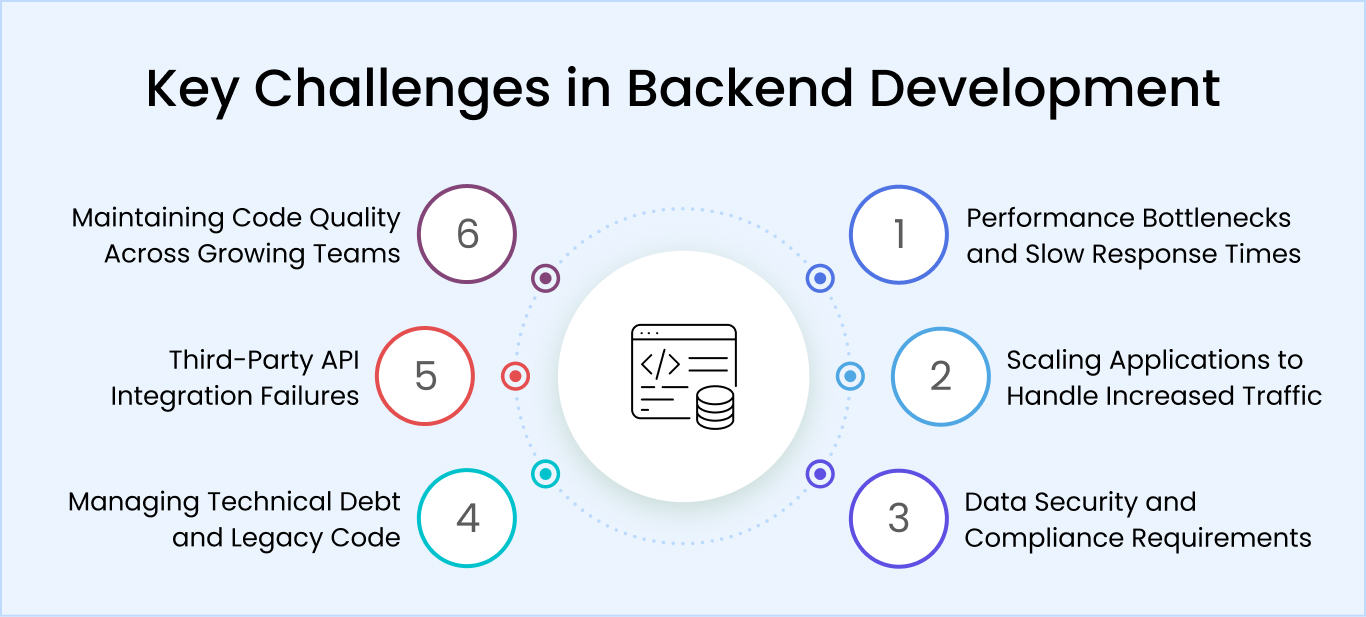
Performance bottlenecks and slow response times
The problem
Applications become sluggish under load, taking several seconds to respond to user requests. Slow database queries, inefficient code, or inadequate server resources create frustrating user experiences and high bounce rates.
The solution
Frequently accessed data should be stored in fast memory caches, and database indexes should be added to speed up searches, reducing the need for repetitive queries. Slow code can be identified and optimized using profiling tools, and images or files should be served through content delivery networks for faster access.
Scaling applications to handle increased traffic
The problem
As user bases grow, applications struggle to handle increased concurrent requests. Single-server architectures hit resource limits, causing crashes during traffic spikes, particularly during marketing campaigns or peak usage times.
The solution
Multiple servers can be added and traffic distributed between them with load balancers, while systems should be designed so that any server can handle any request, and read/write database operations are separated.
Additionally, setting up automatic server scaling ensures more capacity is added during high traffic and removed when demand drops, maintaining efficiency and reliability.
Data security and compliance requirements
The problem
Backend systems handle sensitive user data, making them prime targets for cyber attacks that cause major financial and reputational damage. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS adds further complexity to secure development.
The solution
To address these risks, developers should encrypt all sensitive data during storage and transmission and implement secure login systems with two-factor authentication. It is also vital to validate all user inputs, update software regularly to fix vulnerabilities, and conduct security audits and penetration testing.
Managing technical debt and legacy code
The problem
Quick fixes and shortcuts accumulate over time, creating tangled, hard-to-maintain codebases. Legacy systems built with outdated technologies make adding features difficult and risky, slowing development velocity and increasing bugs.
The solution
Set aside regular time to improve code quality and document how legacy systems work without changing functionality, while also writing tests before modifying old code to catch potential problems. Plan gradual migrations to modern technologies instead of risky complete rewrites, and enforce coding standards to prevent new issues in the future.
Third-party API integration failures
The problem
External services your backend depends on experience downtime, change APIs without notice, or introduce breaking changes. These failures cascade through your system, causing errors that users experience directly.
The solution
Implement automatic retry mechanisms for temporary failures, use circuit breakers that stop calling failing services, and switch to backup options. Monitor service status pages for planned maintenance and store API responses in cache when appropriate, reducing dependency on external services.
Maintaining code quality across growing teams
The problem
As teams expand, inconsistent coding styles, lack of documentation, and poor communication create confusion. Different developers solve similar problems differently, making codebases harder to understand and maintain.
The solution
Set and automatically enforce coding standards, while also requiring code reviews where developers examine each other’s work before merging changes. Maintain clear documentation that explains system design and development processes, use version control with descriptive commit messages, and hold regular knowledge-sharing sessions to promote continuous learning across the team.
Common Backend Development Use Cases You Should Know
Different applications demand different backend capabilities. Knowing the common use cases can guide you in building systems that meet performance, security, and scalability needs.
eCommerce platforms requiring secure transactions
eCommerce platforms need backends managing shopping carts, inventory tracking, payment processing, and order fulfillment. These systems must handle thousands of concurrent transactions securely while maintaining real-time product availability across multiple channels.
SaaS platforms serving multiple customers
SaaS platforms serve thousands of customers from shared infrastructure while keeping each customer’s data completely isolated. They manage subscription billing and control feature access based on different pricing tiers and user permissions.
Real-time applications requiring instant updates
Chat platforms and collaboration tools need instant message delivery, live presence indicators, and real-time updates without page refreshes. These applications maintain persistent connections for thousands of simultaneous users across different devices.
Data-intensive applications requiring analytics
Analytics platforms process massive data volumes and generate insights from user behavior. They create real-time dashboards and run complex queries without impacting transactional operations or slowing down user-facing application performance.
Building a great backend system often requires partnering with the right development team. The coming section talks about how to evaluate potential partners and make the best choice for your project.
How to Choose the Right Backend Development Partner for Your Project
Selecting the right backend development partner directly impacts project success, timeline, and long-term maintainability. Here are the key steps to evaluate potential partners effectively.
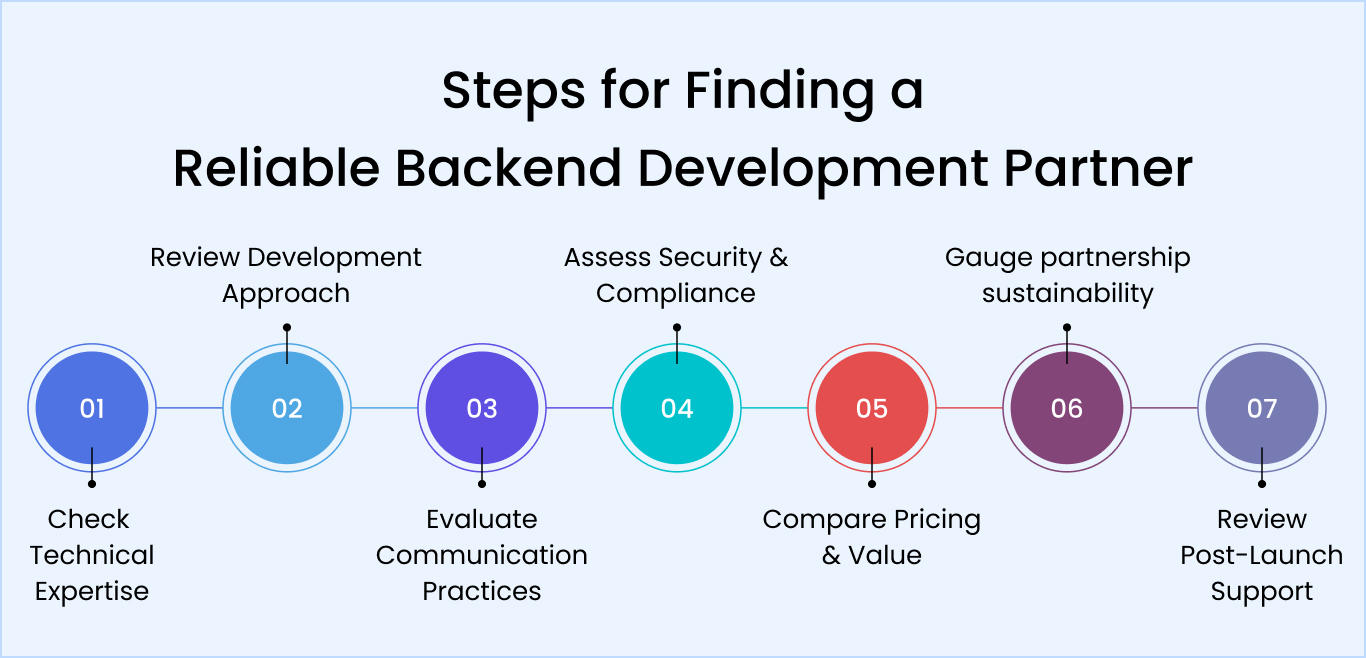
Assess technical expertise and portfolio
Review completed projects demonstrating complexity similar to your requirements. Evaluate their experience with your required technologies, frameworks, and cloud platforms.
Ask specific questions about their approach to database design, API architecture, and performance optimization. Request code samples or conduct technical interviews assessing actual capabilities beyond marketing claims.
Evaluate the development process and methodology
Understand how teams approach projects through their development methodology. Ask about sprint planning, milestone definitions, quality assurance processes, and how they handle scope changes or unexpected challenges.
Teams with structured processes deliver predictable results and handle complexity professionally. Inquire about their code review practices, testing standards, and documentation approach, ensuring maintainability.
Verify communication and collaboration practices
Assess responsiveness during initial conversations and understand their communication channels, meeting cadence, and reporting structure. Determine whether you have direct developer access or only communicate through account managers.
Request references from previous clients, asking specifically about communication quality and responsiveness during challenges. Effective communication prevents misunderstandings and keeps projects on track.
Review security and compliance experience
Verify their security implementation standards, code review processes focused on security, and experience with penetration testing. If your project requires specific compliance certifications like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, ensure they follow necessary protocols.
Request documentation of their security practices and data protection policies protecting your business from costly breaches.
Compare pricing models and value propositions
Understand different pricing models, including fixed-price contracts, time and material arrangements, or dedicated team models. Request detailed proposals breaking down costs by project phase or feature set.
Compare not just total cost but value delivered, as the cheapest option often results in higher long-term costs due to quality issues or technical debt.
Consider long-term partnership potential
Choose partners capable of supporting your system as it evolves beyond initial launch. Discuss their approach to knowledge transfer, documentation, and training your internal team.
Ask about their capacity to scale support as your needs grow and inquire about their technology evolution strategy, ensuring systems stay updated with security patches and performance improvements.
Examine post-launch support offerings
Clarify what post-deployment support includes, such as bug fixes, performance monitoring, security updates, and feature additions. Understand response times for critical issues and the process for requesting changes or enhancements. Partners viewing projects as long-term relationships invest in your success beyond immediate deliverables.
Partner With Experts Who Understand Your Backend Vision
With 15+ years of experience and 1,200+ successful projects, Space-O Technologies has helped startups and enterprises build backends that power innovation and scale effortlessly.
Build a Scalable, Future-Ready Backend with Space-O Technologies
A well-architected backend is the engine that drives every high-performing digital product, ensuring speed, security, and seamless user experiences. From managing massive data loads to enabling real-time interactions, your backend determines how efficiently your application scales and evolves with your business.
But building a powerful backend isn’t just about writing code. It’s about designing a system that supports your product’s long-term vision. That’s where the right development partner makes all the difference.
At Space-O Technologies, we specialize in building robust, scalable, and secure backend systems tailored to your business goals. With 15+ years of experience and 1,200+ clients served globally, our team has delivered backend solutions that balance performance, reliability, and flexibility.
Leveraging technologies like Node.js, Python, Java, Go, PHP, and cloud-native architectures, we design systems optimized for scalability, seamless integrations, and future innovation. Want to know more? Get a free consultation with our backend development experts today.
Frequently Asked Questions On Backend Development
What is backend development?
Backend development refers to server-side programming that powers websites and applications. It handles data storage, business logic, authentication, and server operations, managing databases and integrating with external services.
What’s the difference between frontend and backend development?
Frontend creates the user interface people see and interact with using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Backend handles server logic, databases, and application functionality using server-side languages, processing data and business logic.
What database should I use for backend development?
Use PostgreSQL or MySQL for structured data with complex relationships. Choose MongoDB for flexible schemas and rapid development. Redis works for caching and session storage. Consider data structure, scalability needs, and query patterns.
How to ensure the backend application’s security?
You can secure your backend by implementing encrypted data storage and transmission, secure authentication using OAuth or JWT tokens, input validation preventing SQL injection and XSS attacks, and conducting regular security audits following OWASP guidelines.
What’s the future of backend development?
Backend development is evolving towards serverless architectures, microservices, and cloud-native solutions. AI integration, GraphQL APIs, and edge computing shape modern backends as demand for developers continues growing.
“`html



